Table of Contents
Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
📘 Chapter: Carbon Compounds
Class: 10th SSC (Maharashtra Board)
🔴 MOST IMPORTANT TOPICS (EXAM POINT OF VIEW)
1️⃣ Covalent Bonding in Carbon
- Why carbon forms covalent bonds
- Electron sharing
- Properties of covalent compounds
2️⃣ Versatile Nature of Carbon ⭐⭐⭐
- Catenation
- Tetravalency
- Long chain formation
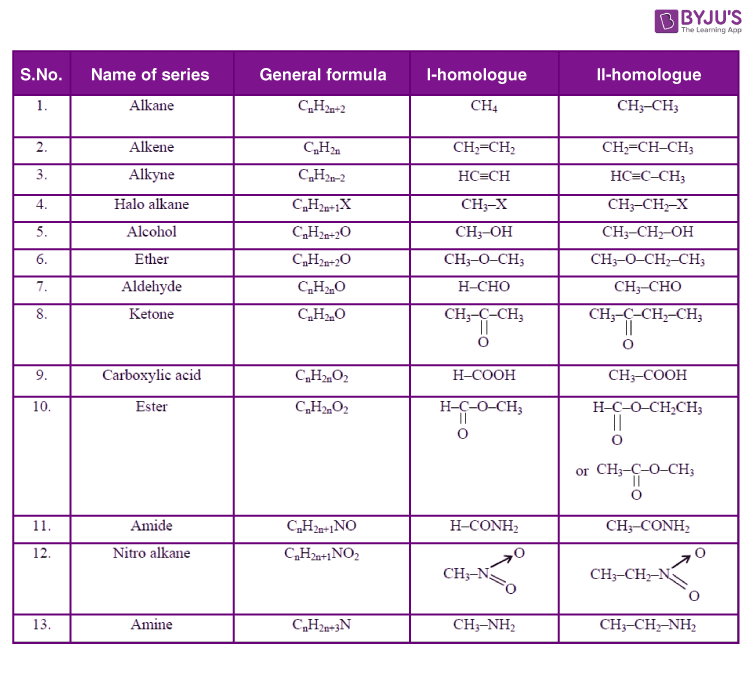
3️⃣ Homologous Series ⭐⭐⭐
- Definition
- Characteristics
- Example (Alkanes / Alcohols)
4️⃣ Functional Groups ⭐⭐⭐
- –OH, –COOH, –CHO, –CO–, –COO–
- Identification
- Naming of compounds
5️⃣ Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds (IUPAC) ⭐⭐⭐
- Rules
- Prefix, suffix
- Examples
6️⃣ Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes ⭐⭐⭐
- General formula
- Saturated vs Unsaturated
- Chemical properties
7️⃣ Ethanol & Ethanoic Acid ⭐⭐⭐⭐
- Preparation
- Properties
- Uses
- Reactions
8️⃣ Soaps and Detergents ⭐⭐⭐⭐
- Cleaning action
- Structure
- Difference between soap & detergent
Board exams mein aksar Electron Dot Structures, Functional Groups, aur Homologous Series par sawal aate hain.
1. Bonding in Carbon (Covalent Bond)
Carbon ka atomic number 6 hai (Configuration: 2, 4). Yeh 4 electrons share karke stable banta hai, jise Tetravalency kehte hain.
- Methane ($CH_4$) Electron Dot Structure: * Center mein ek ‘C’ draw karein aur uske chaaro taraf 4 ‘H’.
- C aur H ke beech mein do dots (:) dikhayein jo sharing dikhate hain.
- Ethane ($C_2H_6$) Structure: * Dono Carbon atoms ke beech single bond ($C-C$).
2. Hydrocarbons ka Classification
Exam mein inka fark aur general formula pucha jata hai:
| Type | Bond Type | General Formula | Example |
| Alkanes | Single Bond ($C-C$) | $C_nH_{2n+2}$ | Methane, Ethane |
| Alkenes | Double Bond ($C=C$) | $C_nH_{2n}$ | Ethene, Propene |
| Alkynes | Triple Bond ($C\equiv C$) | $C_nH_{2n-2}$ | Ethyne (Acetylene) |
3. Functional Groups (Very Important for Labeling)
SSC Board mein yeh table yaad karna zaroori hai:
- Alcohol: $-OH$ (Suffix: -ol) → e.g., Ethanol
- Aldehyde: $-CHO$ (Suffix: -al) → e.g., Ethanal
- Ketone: $-CO-$ (Suffix: -one) → e.g., Propanone
- Carboxylic Acid: $-COOH$ (Suffix: -oic acid) → e.g., Ethanoic acid
- Halogen: $-Cl, -Br, -I$ (Prefix: Chloro, Bromo)
4. Important Cyclic & Branch Structures
- Cyclohexane ($C_6H_{12}$): 6 Carbon atoms ka ek hexagon ring.
- Benzene ($C_6H_6$): Hexagon ring jisme alternate double bonds hote hain.
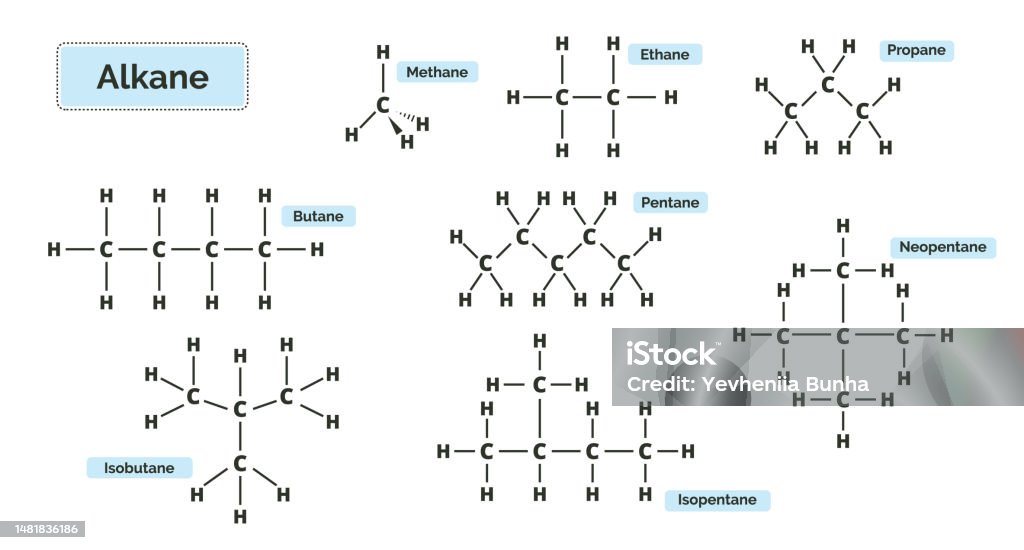
- Structural Isomers: Jaise $n-butane$ (straight chain) aur $isobutane$ (branched chain). Inka molecular formula same hota hai par structure alag.
5. Allotropes of Carbon
Inka diagrammatic representation short notes mein aata hai:
- Diamond: Tetrahedral structure (Strong).
- Graphite: Hexagonal layers (Slippery, conducts electricity).
- Fullerene ($C_{60}$): Football jaisa structure (Buckminsterfullerene).
Revision Tip: Board exam mein Electron Dot Structure pencil se neat banayein aur circles bilkul clear hone chahiye.
TRY DRAWING THE ELECTRON DOT STRUCTURE OF ETHYNE
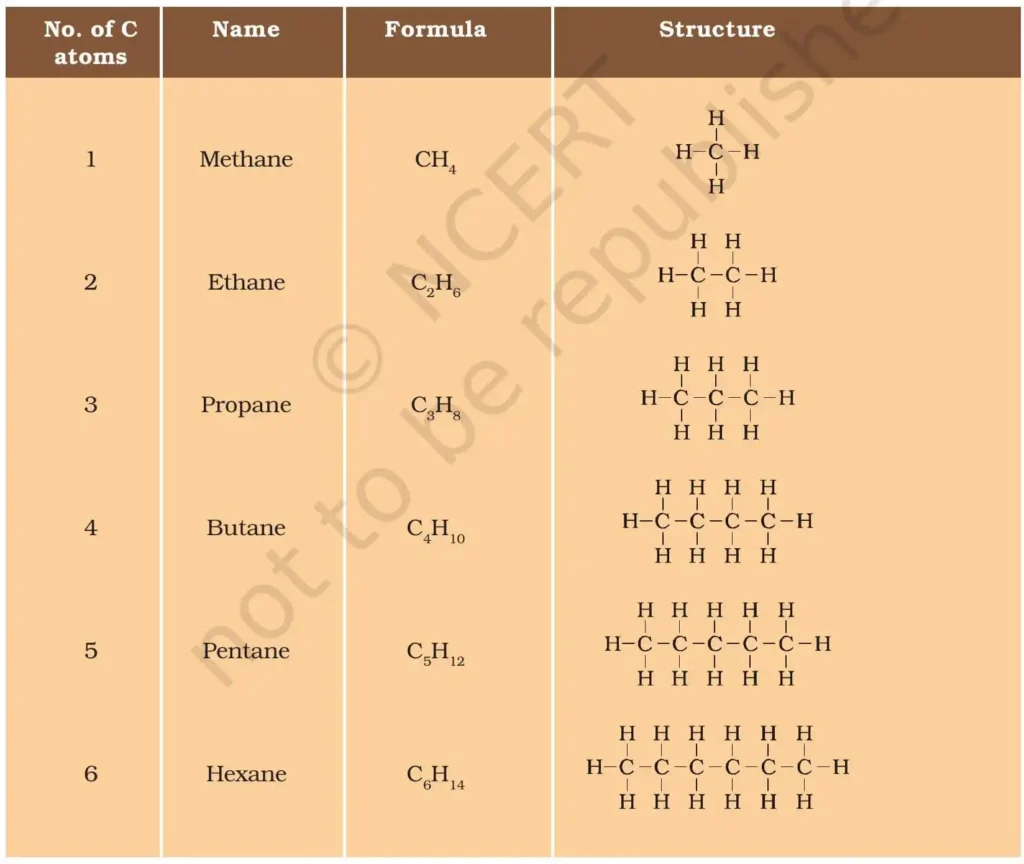
Formulae and Structures of Saturated Compounds of Carbon and Hydrogen
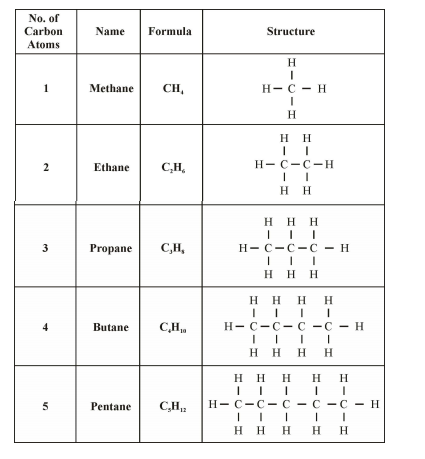
Formulae and structures of saturated compounds of carbon and hydrogen
📝 IMPORTANT EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
Q1. Why carbon forms covalent bonds?
Answer:
Carbon has 4 valence electrons. It cannot lose or gain 4 electrons easily, so it shares electrons with other atoms to complete its octet, forming covalent bonds.
Q2. Explain the versatile nature of carbon.
Answer:
Carbon shows versatility due to:
- Catenation – ability to form long chains with itself
- Tetravalency – ability to form four covalent bonds
This results in millions of carbon compounds.
Q3. What is homologous series?
Answer:
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds:
- Having same functional group
- Same general formula
- Successive members differ by –CH₂ unit
Example: Alkanes (CH₄, C₂H₆, C₃H₈)
Q4. Define functional group with examples.
Answer:
Functional group is an atom or group of atoms that decides chemical properties of a compound.
| Functional Group | Name |
|---|---|
| –OH | Alcohol |
| –COOH | Carboxylic acid |
| –CHO | Aldehyde |
| –CO– | Ketone |
Q5. Write differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
| Saturated | Unsaturated |
|---|---|
| Single bond | Double / triple bond |
| Alkanes | Alkenes & Alkynes |
| Less reactive | More reactive |
Q6. Write properties and uses of Ethanol.
Properties:
- Colorless liquid
- Soluble in water
- Burns with blue flame
Uses:
- As fuel
- In medicines
- As solvent
Q7. Write properties and uses of Ethanoic Acid.
Properties:
- Sour taste
- Turns blue litmus red
- Reacts with carbonates
Uses:
- Vinegar
- Food preservative
- Manufacture of esters
Q8. Explain cleaning action of soap.
Answer:
Soap molecules have:
- Hydrophilic head (water-loving)
- Hydrophobic tail (oil-loving)
They form micelles that trap grease and wash it away with water.
Q9. Difference between soap and detergent.
| Soap | Detergent |
|---|---|
| Works in soft water | Works in hard water |
| Forms scum | No scum |
| Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable |
Q10. Write general formula:
- Alkane → CnH₂n+2
- Alkene → CnH₂n
- Alkyne → CnH₂n−2
⭐ VERY IMPORTANT DIAGRAMS (PRACTICE)
- Soap micelle structure
- Ethanol structure
- Ethanoic acid structure
- Covalent bond formation
📌 LAST-MINUTE BOARD EXAM TIPS – Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
✔ Learn functional groups table
✔ Practice IUPAC naming
✔ Revise ethanol & ethanoic acid reactions
✔ Diagrams = 2–3 easy marks
🟢 MCQs (Most Expected) – Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
1. Carbon forms covalent bonds because it has:
A) 2 valence electrons
B) 3 valence electrons
C) 4 valence electrons
D) 8 valence electrons
✅ Answer: C
2. Which property explains long chain formation in carbon?
A) Tetravalency
B) Isomerism
C) Catenation
D) Combustion
✅ Answer: C
3. General formula of alkenes is:
A) CnH₂n+2
B) CnH₂n
C) CnH₂n–2
D) CnHn
✅ Answer: B
4. –COOH functional group is present in:
A) Alcohol
B) Aldehyde
C) Ketone
D) Carboxylic acid
✅ Answer: D
5. Ethanol reacts with sodium to produce:
A) Hydrogen
B) Oxygen
C) Carbon dioxide
D) Nitrogen
✅ Answer: A
6. Which one is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
A) Methane
B) Ethane
C) Ethene
D) Propane
✅ Answer: C
7. Soap does not work properly in hard water because:
A) Forms foam
B) Forms scum
C) Is acidic
D) Is basic
✅ Answer: B
8. Vinegar contains:
A) Methanol
B) Ethanol
C) Ethanoic acid
D) Formic acid
✅ Answer: C
9. Functional group of aldehyde is:
A) –CO–
B) –CHO
C) –OH
D) –COOH
✅ Answer: B
10. Detergents are preferred over soaps because:
A) Cheap
B) Work in hard water
C) Natural
D) Less effective
✅ Answer: B
🔢 NUMERICAL-TYPE QUESTIONS (Very Important)
Q1. Find molecular formula of alkane with 5 carbon atoms.
Solution:
General formula of alkane = CnH₂n+2
n = 5
∴ Molecular formula = C₅H₁₂
Q2. Find molecular formula of alkene having 6 carbon atoms.
Answer:
CnH₂n = C₆H₁₂
Q3. An organic compound contains 3 carbon atoms and is saturated. Find its molecular formula.
Answer:
Alkane → C₃H₈
Q4. Find molecular formula of alkyne having 4 carbon atoms.
Answer:
CnH₂n−2 = C₄H₆
Q5. Name the compound having formula C₂H₅OH.
Answer: Ethanol
🟠 BOARD-PATTERN LONG ANSWERS (5 Marks)
Important link: https://sanskartutorials.in/class-10-science-notes-hindi-maharashtra-board/
Q1. Explain versatile nature of carbon.
Answer:
Carbon shows versatility due to following reasons:
- Catenation: Carbon atoms form long chains, branches and rings.
- Tetravalency: Carbon forms four covalent bonds with other atoms.
- Strong covalent bonds: Carbon-carbon bonds are strong and stable.
Due to these properties, carbon forms a large number of organic compounds.
Q2. What is homologous series? Write its characteristics.
Answer:
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having same functional group and general formula.
Characteristics:
- Same chemical properties
- Gradual change in physical properties
- Successive members differ by –CH₂ unit
- Same method of preparation
Q3. Explain properties, preparation and uses of Ethanol.
Answer:
Properties:
- Colorless liquid
- Soluble in water
- Burns with blue flame
Preparation:
By fermentation of sugar solution using yeast.
Uses:
- Fuel
- Medicines
- Solvent
Q4. Explain cleaning action of soap with diagram.
Answer:
Soap molecules have:
- Hydrophilic head
- Hydrophobic tail
They form micelles in water. The hydrophobic tail traps oil while hydrophilic head remains in water. Dirt is removed while washing.
(Diagram compulsory in exam)
Q5. Write differences between soaps and detergents.
Answer:
| Soap | Detergent |
|---|---|
| Works in soft water | Works in hard water |
| Forms scum | No scum |
| Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable |
| Less effective | More effective |
Q6. Explain IUPAC naming of organic compounds.
Answer:
Steps:
- Longest carbon chain selection
- Numbering the chain
- Naming functional group
- Writing prefix and suffix
Example:
CH₃–CH₂–OH → Ethanol
📌 EXAM SCORING STRATEGY – Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
✔ MCQs = fast & sure marks
✔ Numericals = easy formula-based
✔ Long answers = write points + diagram
🔴 IMPORTANT REACTIONS – Carbon Compounds
(Learn with balanced chemical equations)
1️⃣ Combustion Reactions ⭐⭐⭐
(Very common – 1–2 marks)
General Reaction:
Hydrocarbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Heat
Example:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + Heat
2️⃣ Oxidation of Ethanol ⭐⭐⭐⭐
Reaction:
C₂H₅OH + [O] → CH₃COOH + H₂O
Oxidising agents:
- Alkaline KMnO₄
- Acidified K₂Cr₂O₇
3️⃣ Reaction of Ethanol with Sodium ⭐⭐⭐
2C₂H₅OH + 2Na → 2C₂H₅ONa + H₂↑
Observation:
- Hydrogen gas evolves
- Effervescence seen
4️⃣ Esterification Reaction ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (VERY IMPORTANT)
Reaction:
Ethanol + Ethanoic acid → Ester + Water
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH
→ CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
Conditions:
- Conc. H₂SO₄
- Heat
Product: Ethyl ethanoate (pleasant smell)
5️⃣ Saponification Reaction ⭐⭐⭐⭐
Reaction:
Ester + NaOH → Soap + Alcohol
CH₃COOC₂H₅ + NaOH
→ CH₃COONa + C₂H₅OH
6️⃣ Reaction of Ethanoic Acid with Sodium ⭐⭐⭐
2CH₃COOH + 2Na
→ 2CH₃COONa + H₂↑
7️⃣ Reaction of Ethanoic Acid with Sodium Carbonate ⭐⭐⭐
2CH₃COOH + Na₂CO₃
→ 2CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂↑
Test:
CO₂ turns lime water milky.
8️⃣ Reaction of Ethanoic Acid with Sodium Bicarbonate ⭐⭐⭐⭐
CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃
→ CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂↑
9️⃣ Dehydration of Ethanol ⭐⭐⭐
Reaction:
C₂H₅OH → C₂H₄ + H₂O
Conditions:
- Conc. H₂SO₄
- 170°C
Product: Ethene
🔟 Addition Reaction (Unsaturated Hydrocarbons) ⭐⭐⭐
Example:
C₂H₄ + H₂ → C₂H₆
Condition:
- Nickel catalyst
1️⃣1️⃣ Substitution Reaction (Alkanes) ⭐⭐⭐
Example:
CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl
Condition:
- Sunlight
1️⃣2️⃣ Oxidation of Ethanoic Acid ⭐⭐
Ethanoic acid + Oxidising agent
→ No reaction
(Used as distinguishing test)
📌 REACTIONS YOU MUST REMEMBER BY HEART
✔ Ethanol + Sodium
✔ Ethanol → Ethanoic acid
✔ Esterification
✔ Ethanoic acid + Carbonate
✔ Combustion of hydrocarbons
📝 Board Exam Tip – Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
- Equation + condition + name likhna = full marks
- Esterification reaction ke sath smell point zaroor likho
- Gas reaction me ↑ symbol use karo
🔴 NAME THE REACTION – IMPORTANT QUESTIONS – carbon compounds important reactions class 10
Q1.
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH
→ CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
Name the reaction:
✅ Esterification
Q2.
2C₂H₅OH + 2Na
→ 2C₂H₅ONa + H₂↑
Name the reaction:
✅ Reaction of ethanol with sodium
(Chemical reaction producing hydrogen gas)
Q3.
CH₄ + 2O₂
→ CO₂ + 2H₂O + Heat
Name the reaction:
✅ Combustion reaction
Q4.
C₂H₄ + H₂
→ C₂H₆
Name the reaction:
✅ Addition reaction
Q5.
CH₄ + Cl₂
→ CH₃Cl + HCl (in sunlight)
Name the reaction:
✅ Substitution reaction
Q6.
CH₃COOC₂H₅ + NaOH
→ CH₃COONa + C₂H₅OH
Name the reaction:
✅ Saponification reaction
Q7.
C₂H₅OH → C₂H₄ + H₂O
(Conc. H₂SO₄, 170°C)
Name the reaction:
✅ Dehydration reaction
Q8.
C₂H₅OH + [O]
→ CH₃COOH + H₂O
Name the reaction:
✅ Oxidation reaction
Q9.
CH₃COOH + Na₂CO₃
→ CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂↑
Name the reaction:
✅ Acid–carbonate reaction
Q10.
CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃
→ CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂↑
Name the reaction:
✅ Acid–bicarbonate reaction
Q11.
Ester + Alkali → Soap + Alcohol
Name the reaction:
✅ Saponification
Q12.
Hydrocarbon + Oxygen
→ CO₂ + H₂O + Heat
Name the reaction:
✅ Combustion
🟢 MOST FREQUENTLY ASKED IN BOARD
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Esterification
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Saponification
⭐⭐⭐ Addition reaction
⭐⭐⭐ Substitution reaction
⭐⭐ Oxidation of ethanol
📌 EXAM TIP – Carbon compounds class 10 ssc board notes
👉 “Name the reaction” me sirf reaction ka naam likhna hota hai
👉 Agar space mile, conditions likh do → extra impression
👉 Arrow ke upar Ni / Sunlight / Conc. H₂SO₄ likhna na bhoolen
❓ FAQ – Carbon Compounds (Exam Focused)
Q1. What are carbon compounds in Class 10?
Answer:
Carbon compounds are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. They mainly show covalent bonding.
Q2. Why is carbon called a versatile element?
Answer:
Carbon is versatile due to its catenation and tetravalency, which allows it to form long chains and millions of compounds.
Q3. Which topics are most important in Carbon Compounds for SSC exams?
Answer:
Important topics include:
- Versatile nature of carbon
- Homologous series
- Functional groups
- Ethanol and ethanoic acid
- Soaps and detergents
Q4. Which reactions are most important in Carbon Compounds?
Answer:
Esterification, saponification, combustion, oxidation of ethanol, addition and substitution reactions are most important.
Q5. Are carbon compounds numericals asked in SSC board exams?
Answer:
Yes, numericals based on general formula of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes are frequently asked.
⭐ BONUS
📌 This chapter alone can give you 15–20 easy marks if prepared properly.








