Table of Contents
Substances in Common Use – Class 9 Science (Maharashtra Board)
Substances in Common Use Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Maharashtra Board
This chapter explains materials used in daily life such as metals, non-metals, fuels, polymers, ceramics, glass, and alloys, their properties and applications.
Chapter Overview: Substances in Common Use
(Class 9 Science – Maharashtra Board)

In this chapter, students learn about substances used in daily life and their properties, preparation, and uses. The chapter mainly focuses on metals, non-metals, alloys, acids, bases, and salts that are commonly used at home and in industries.
Students study the physical and chemical properties of these substances and understand why a particular substance is suitable for a specific use. The chapter also explains the uses of iron, aluminium, copper, plastics, glass, and chemicals in everyday life.
This chapter helps students connect science with real-life applications and builds a foundation for understanding materials, chemistry, and industrial processes.
1. Fill in the blanks.
a. The number of molecules of water of crystallization in washing soda is …………….…. .
b. The chemical name of baking soda is …………….…. .
c. …………….…. is used in treatment of hyperthyroidism.
d. The chemical name of Teflon is …………….…. .
Answer:
a. 10
b. Sodium bicarbonate
c. Iodine -123
d. Polytetra fluoroethylene (C2F4)n
a. The number of molecules of water of crystallization in washing soda is …………….…. .
b. The chemical name of baking soda is …………….…. .
c. …………….…. is used in treatment of hyperthyroidism.
d. The chemical name of Teflon is …………….…. .
Answer:
a. 10
b. Sodium bicarbonate
c. Iodine -123
d. Polytetra fluoroethylene (C2F4)n
3. Write answers to the following
a. What is meant by radioactivity?
Answer:
- Elements with a high atomic number such as uranium, thorium, radium have a property of spontaneously emitting invisible, highly penetrating and high energy radiation.
- This property is called radioactivity.
- A substance having this property is called a radioactive substance.
b. When is said to be the nucleus unstable?
Answer:
- It is the balance of protons and neutrons in a nucleus which determines whether a nucleus will be stable or unstable.
- Too many neutrons or protons upset this balance disrupting the binding energy from the strong nuclear forces making the nucleus unstable.
c. Which diseases are caused by artificial food colours?
Answer:
Diseases like ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) can affect children due to excessive consumption of foods with added food colours.
d. Where in the industrial field is radioactivity used?
Answer:
Industrial field Radiography
Groceries
- Internal cracks and voids in cast iron articles and iron solder can be detected with the help of gamma rays.
- For this purpose, isotopes like cobalt-60, iridium-192 are used in the radiography camera.
- This technique is used for detecting flaws in metal work.
Measurement of thickness, density and level
- It is necessary to maintain the required thickness in the manufacture of aluminium, plastic, iron sheets of differing thickness.
- In the manufacturing process, a radioactive substance is placed on one side and an instrument to measure radiation on the other.
- The radiation read by the measuring instrument varies with the thickness of the sheet.
- Material inside a packing can also be examined by the same technique.
Luminescent paint and radio luminescence:
- The radioactive substances radium, promethium, tritium with some phosphor are used to make certain objects visible in the dark, for example, the hands of a clock, and certain other objects.
- Krypton-85 is used in HID (High-Intensity Discharge) lamps while promethium – 147 is used in portable X-ray units as the source of beta rays.
Use in Ceramic articles:
- Luminous colours are used to decorate ceramic tiles, utensils, plates, etc.
- Earlier uranium oxide was used in these paints.
e. Write down properties of teflon.
Answer:
Properties of teflon :
- The atmosphere and chemical substances have no effect on Teflon.
- Neither water nor oil will stick to Teflon coated articles.
- High temperatures do not affect Teflon as its melting point is 327 °C.
- Teflon coated articles are easy to clean.
f. What type of colours will you use to celebrate ecofriendly Rang Panchami? Why?
Answer:
- We regularly use artificial colours on Rang Panchami.
- The red colour used on Rang Panchami is very dangerous. It contains a high proportion of mercury in it.
- This poses risks like blindness, skin cancer, asthma, itching of the skin, permanent blocking of sweat pores, etc.
- Therefore, it is necessary to use eco-friendly colours.
- We will prepare colours for Rang Panchami from natural resources such as beet root, flowers of flame of forest, spinach, flame tree (gulmohar) and protect your health by using these.
g. Why has the use of methods like Teflon coating become more common?
Answer:
The use of methods like Teflon coating became more common because of following properties of teflon:
Buy vitamins and supplements
- The atmosphere, rain water and chemical substances have no effect on Teflon.
- Neither water nor oil will stick to Teflon coated articles.
- High temperatures do not affect Teflon as its melting point is 327 °C.
- Teflon coated articles are easy to clean.
- Teflon is a poor conductor of electricity.
4. Give a scientific explanation
a. Bleaching powder has the odour of chlorine.
Answer:
- Bleaching powder undergoes slow decomposition due to the carbon dioxide in air and chlorine gas is released.
- Bleaching powder gets its property because of this release of chorine gas.

b. The hard water of a well becomes soft on adding washing soda to it.
Answer:
- The hard water from a well or a bore-well becomes soft on adding washing soda and we come to know this from the lather formed on it.
- The hardness of water is due to the presence of chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium in it.
- Na2CO3 is added to it to soften such water and make it suitable for use.
- The reaction with Na2CO3 causes the formation of insoluble carbonate salts of magnesium and calcium.
MgCl2(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → MgCO3(s) + 2 NaCl(s)
c. Soap forms a precipitate in hard water.
Answer:
- When soap is mixed with hard water, calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids are formed.
- These being water insoluble, they form a precipitate and that is why lather is not formed.
d. The particles of powder are given an electric charge while spraying them to form the powder coating.
Answer:
- Powder coating is a method of applying a layer harder than paint on the surface of an iron object to prevent rusting.
- In this method, a polymer resin, a pigment and some other ingredients are melt, mixed, cooled and ground into a uniform powder.
- This powder is sprayed on the polished metal surface by electrostatic spray deposition (ESD).
- In this method, the particles of the powder are given an electrostatic charge due to which a uniform layer of the powder sticks to the metal surface.
- Then the object is heated in the oven along with the coating.
- A chemical reaction occurs in the layer, resulting in the formation of long cross-linked polymeric chains.
e. The aluminium article is used as an anode in the anodising process.
Answer:
- A protective layer is formed naturally on the surface of aluminium metal by reaction with oxygen in air.
- In the anodizing process, this layer is made of the desired thickness. Anodizing is done by electrolysis.
- Dilute Sulphuric acid is taken in the electrolytic cell and the aluminium article is dipped in it as the anode.
- When an electric current is passed, hydrogen gas is released at the cathode and oxygen gas at the anode.
- A reaction with oxygen occurs and a layer of hydrated aluminium oxide is formed on the anode. Therefore, aluminium article is used as an anode in the anodizing process.
f. When the radiation coming out from certain radioactive substance is passed through an electric field, marks are found at three places on the photographic plate placed in its path.
Answer:
(i) When the radiation coming out from certain radioactive substance is passed through an electric field, marks are found at three places on the photographic plate placed in its path. This is because the radiation coming out from radioactive substance are of three types Alpha rays, Beta rays and Gamma rays.
(ii) The rays which get deviated slightly towards negatively charged plate are called alpha rays. They get deviated towards negatively charged plate because they are made of positively charged particles, called as alpha particles (He++).
(iii) The rays which get deviated substantially towards the positively charged plate are called beta rays. They get deviated towards a positively charged plate because they are made of negatively charged particles called as beta particles (e-).
(iv) The rays which do not deviate at all are called gamma rays. They are uncharged electromagnetic radiation. Hence, marks are found at three places on the photographic plate. (For diagram refer Fig. 14 .2 from Q. 4(3))
g. A certain type of ceramic tiles are fixed on the outer layer of a space shuttle.
Answer:
(i) Each shuttle is covered by more than 24,000 of the six- by six-inch advance ceramic tiles. This tiles withstand high temperatures without decomposing. They are brittle, water-resistant and electrical insulator. Most of the tiles are made of silica fibres, which are produced from high-grade sand (SiO2).
(ii) Silica is an excellent insulator because it transports heat slowly. When the outer portion of a tile gets hot, the heat takes a long time to work its way down through the rest of the tile to the shuttle’s skin. The tiles keep the orbiter’s aluminium skin at 350 degrees or less.
(iii) The silica fibers are mixed with water and chemicals, and the mixture is poured into molds, which are zapped in microwave ovens at 2,350°C to fuse the silica fibres. Tiles are too brittle to attach to the orbiter directly.
(iv) The shuttle’s skin contracts slightly while in orbit, then expands during re-entry.
(v) In addition, the stresses of launch and re-entry cause the skin to flex and bend. Such motions could easily crack the tiles or shake them off. To keep them in place, workers glue the tiles to flexible felt-like pads, then glue the pads to the orbiter.
5. Write answers to the following
a. Write about artificial food colours, the substances used in them and their harmful effects.
Answer:
(a) Artificial food colour and substances in them.
Groceries
- Food colours are mixed in most soft drinks and foodstuffs available in the market.
- These food colours are in the form of powders, gels and pastes.
- Food colours are used in domestic as well as commercial products.
- Certain colours and essences are added to ice cream, ice candies, sauce, fruit juices, cold drinks, pickles, jams and jelly.
- Food colours are often found to be added to packaged meat (chicken, mutton), chilli powder, turmeric, sweets and other similar substances so as to give them a good colour.
- Tetrazene, sunset yellow are artificial food colours used extensively.
(b) Harmful effects of artificial food colours
- Food colours added to pickles, jam and sauce contain small quantities of lead and mercury. These can be harmful for those who consume these products on a regular basis.
- Diseases like ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) can affect children due to excessive consumption of foods with added food colours.
b. What is meant by water of crystallization? Give examples of salts with water of crystallization, and their uses.
Answer:
The exact number of water molecules which are chemically bonded to a molecule of a salt within a hydrated crystalline compound is called as water of crystallization are:
Some substances in our daily use which contain water of crystallization are:
- Alum (Potash alum – K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O)
- Borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O)
- Epsom salt (Magnesium sulphate MgSO4.7H2O)
- Barium chloride (BaCl2.2H2O)
- Sodium sulphate (Glauber’s salt Na2SO4.10 H2O)
- Blue vitriol (Copper Sulphate – CuSO4.5H2O)
Uses of these salts are as given below:
(i) Alum (Potash alum – K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O)
- Alum is used in the process of water purification.
- Because of the property of coagulation, the solid impurities in water come together, become heavy and settle to the bottom. As a result, the impure water or muddy above becomes clear.
- Alum powder, found in the spice section of many grocery stores, may be used in pickling recipes as a preservative to maintain fruit and vegetable crispness.
- Alum is used as the acidic component of some commercial baking powders.
- Alum has been used as an after shave treatment.
(ii) Borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O)
- Borax today is used for many cleaning purposes.
- It is used to make homemade laundry detergent.
- It is added as a cleaning boost to any other detergent.
- It even keeps ants and other pests away.
(iii) Epsom salt (Magnesium sulphate MgSO4.7H2O)
- Epsom salt is used as a relaxing magnesium bath soak.
- To grow better vegetables – Add a tablespoon of Epsom salt to the soil below a vegetable plant to boost growth.
(iv) Barium chloride (BaCl2.2H2O)
- In industry, Barium chloride is mainly used in the purification of brine solution in caustic chlorine plants.
- It is also used in the manufacture of heat treatment salts.
- It is used in hardening of steel.
- It is used in the manufacture of pigments.
(v) Sodium sulphate (Glauber’s salt Na2SO4.10H2O)
- In the laboratory, anhydrous Sodium sulphate is widely used as an inert drying agent, for removing traces of water from organic solutions.
- Glauber’s salt, the decahydrate, is used as a laxative.
(vi) Blue vitriol (Copper sulphate CuSO4.5H2O)
- Blue vitriol is used in the blood test for diagnosing anaemia.
- Slaked Time is used with blue vitriol in the Bordeaux mixture which is used as a fungicide on fruits like grapes and musk melon.
c. Write briefly about the three methods of electrolysis of sodium chloride.
Answer:
- When an electric current is passed through a saturated solution of sodium chloride (brine) it is electrolysed and hydrogen gas is released at the cathode while chlorine gas is released at the anode.
- This method is used for production of chlorine gas. In this method an important basic compound NaOH is formed in the cell.
- Chemical reaction
2NaCl + 2H2O → 2NaOH + Cl2 ↑ + H2↑ - When salt is heated to a high temperature (about 800 °C), it melts. This is called the fused state of the salt.
6. Write the uses.
a. Anodizing
b. Powder coating
c. Radioactive substances
d. Ceramic
Answer:
(a) Anodizing : Anodizing is done on aluminum cooking utensils like griddles and cookers.
(b) Powder coating : Powder coating is done on iron objects to prevent rusting. Also, on Plastic and Medium density fibre (MDF) board, to make them highly durable, hard and attractive.
(c) Radioactive substances:
(I) Industrial field:
(i) Industrial Radiography : Internal cracks and voids in cast iron articles and iron solder can be. detected with the help of gamma rays. For this purpose, isotopes like cobalt-60, iridium-192 are used in the radiography camera. This technique is used for detecting flaws in metal work.
(ii) Measurement of thickness, density and level: It is necessary to maintain the required thickness in the manufacture of aluminium, plastic, iron sheets of differing thickness. In the manufacturing process, a radioactive substance is placed on one side and an instrument to measure radiation on the other. The radiation read by the measuring instrument varies with the thickness of the sheet. Material inside a packing can also be examined by the same technique.
(iii) Luminescent paint and radioluminescence:
The radioactive substances radium, promethium, tritium with some phosphor are used to make certain objects visible in the dark, for example, the hands of a clock, and certain other objects. Krypton-85 is used in HID (High Intensity Discharge) lamps while promethium-147 is used in portable X-ray units as the source of beta rays.
Use in Ceramic articles – Luminous colours are used to decorate ceramic tiles, utensils, plates, etc. Earlier uranium oxide was used in these paints.
(II) Field of agriculture :
- The genes and chromosomes that give seeds properties like fast growth, higher productivity, etc. can be modified by means of radiation.
- The radioactive isotope cobalt-60 is used for food preservation.
- Onions, potatoes are irradiated with gamma rays from cobalt-60 to prevent their sprouting.
- Strontium-90 is used as a tracer in the research on various crops.
(III) Medical science:
Groceries
- Polycythemia : The red blood cell count increases in the disease polycythemia. Phosphorus- 32 is used in its treatment.
- Bone cancer : Strontium-89, strontium-90, samarium-153 and radium-223 are used in the treatment of bone cancer.
- Hyperthyroidism : Enlargement of thyroid gland, weight loss in spite of appetite, insomnia are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
- It occurs due to overproduction of hormones by the thyroid gland. Iodine-123 is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.
- Tumour detection : Boron-10, iodine-131, cobalt-60 are used in treatment of brain tumour, while arsenic-74 is used in detection of small tumours in the body.
(d) Ceramic : Pots made by a potter, Mangalore roofing tiles, construction bricks, pottery, terracotta articles are some examples of common ceramic articles that we see around.
7. Write the harmful effects
a. Artificial dye
b. Artificial food colour
c. Radioactive substances
d. Deodorant
Answer:
(a) Artificial dye:
- Dyeing hair can have adverse effects like hair fall, damage to hair texture, burning of skin, adverse effect on eyes, etc.
- Lipstick contains a dye named carmine. It does not affect lips but causes stomach disorders.
- Excessive use of plants for making natural dyes results in deterioration of the environment.
(b) Artificial food colour:
- Food colours added to pickles, jams and sauces contain small quantities of lead and mercury. These can be harmful for those who consume these products on a regular basis.
- Diseases like ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) can affect children due to excessive consumption of foods with added food colours.
(c) Radioactive substances :
- The central nervous system is affected by radioactive radiations.
- Hereditary defects are generated by bombardment of radiation on D.N.A in the body.
- Radioactive radiation can penetrate the skin, and causes diseases like skin cancer, leukemia.
- The radioactive pollutants created due to explosions enter the body through air and it is difficult to control them.
- The radioactive pollutants released in the sea enter the bodies of fishes and through them enter the human body.
- The radioactive paint on the watch can cause cancer.
- The radioactive isotopes strontium-90 can enter the body through plants, fruits, flowers, cereals, milk, etc. and cause diseases like bone cancer, leukemia.
(d) Deodorant:
- Aluminium – Zirconium compounds are the most harmful chemicals in the deodorant. Disorders like headache, asthma, respiratory disorders, heart disease are likely to occur without our knowledge.
- There is a possibility of various skin disorders and also skin cancer due to the aluminium chlorohydrates.
8. Write the chemical formula Bleaching powder, common salt, baking soda, washing soda
Answer:
| Common name | Chemical name |
| Bleaching powder | CaOCl2 |
| Common salt | NaCl |
| Baking soda | NaHCOs |
| Washing soda | Na2CO3.10 H2O |
9. Explain what you see in the following picture
Powder coating

Answer:
- This picture shows powder coating of the given object. Powder coating is a method of applying a layer harder than paint on the surface of an iron object to prevent rusting.
- In this method, a polymer resin, a pigment and some other ingredients are melt mixed, cooled and ground into a uniform powder.
- This powder is sprayed on the polished metal surface by electrostatic spray deposition (ESD).
- In this method, the particles of the powder are given an electrostatic charge due to which a uniform layer of the powder sticks to the metal surface.
- Then the object is heated in the oven along with the coating.
- A chemical reaction occurs in the layer, resulting in the formation of long cross-linked polymeric chains.
- This powder coating is highly durable, hard and attractive. Powder coating can be done on plastic and medium density fibre (MDF) board in day to day use as well.
Intext Questions and Answers
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Substances in Common Use Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall?
Question 1.
What are detergents?
Answer:
- Detergent is a water-soluble cleansing agent which combines with impurities and dirt to make them more soluble, and differs from soap in not forming a scum with the salts in hard water.
- Today, detergents are more likely to be a mixture of synthetic chemicals and additives cooked up in a huge chemical plant and, unlike traditional soap, they’re generally liquids rather than solids.
- Detergents are used in everything from hair shampoo and clothes, washing powder to shaving foam and stain removers.
- The most important ingredients in detergents are chemicals called surfactants – a word made from bits of the words surface-active agents.
Question 2.
What are the important substances that we use in day to day life? For what purposes do we use them?
Answer:
Some of the substances we use in our day to day life and the purpose of using them are as follows:
Toothpaste: for cleaning teeth and maintaining hygienic conditions of mouth.
Soap : for bathing and maintaining hygienic conditions of body.
Natural and artificial fibers : we wear them as clothes to protect our body and many other purposes.
Washing powder: for cleaning clothes. Vegetables, fruits and food grains : they provide us with necessary vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates required for proper functioning of body.
Groceries
Water : very important for our survival and many other functions of day to day life.
Metals : for making buildings, bridges, roads, vehicles, trains, ships, airplanes, utensils etc.
Acids, bases and salts : used for various purposes, for example, Sodium chloride which is used as common salt, a very necessary ingredient of our daily food without which our food is tasteless.
Question 3.
How are the various substances in day to day use classified from the scientific point of view?
Answer:
The various substances in day to day use are classified from the scientific point of view as elements, compounds, mixtures, metals, non-metals, acids, bases and salts.
Question 4.
Which chemicals and apparatus will you use in the laboratory for making soap?
Answer:
For making soap in laboratory following chemicals and apparatus are used :
Chemicals : Vegetable oil (coconut oil, castor oil, soya bean oil etc.)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Salt (Sodium chloride NaCl)
Apparatus :
500 ml glass beaker
Burner
Flat glass tray
Knife
Soaps are essential to personal and public health. They safely remove germs, soils and other contaminants and help us to stay healthy and make our surroundings more pleasant. Soaps are made from fats and oils or their fatty acids.
Buy vitamins and supplements
Take about 20 ml of any vegetable oil (coconut oil, castor oil, soybean oil etc.) in a beaker. Put about 30 – 35 ml of NaOH in it and heat and stir the mixture till a paste is formed. Now add a little salt. Stir again and allow the mixture to cool in a flat glass tray, on cooling it solidifies. Take a knife and cut it in soap bars as per the size required.
Question 5.
What are salts?
Answer:
- Inorganic substances occur naturally in the form of salts rather than acids or bases.
- The ionic compounds which do not contain H+ and OH ions and contain only one kind of cation and anion are called simple salts.
- For example, Na2SO4, K3PO4, CaCl2.
- The sea is said to be a rich source of salts. In fact, the sea is a rich source of several salts of various elements such as chlorine, sodium, magnesium, potassium, calcium, bromine.
- The important salts found in sea water are sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, magnesium sulphate, potassium chloride, calcium carbonate and magnesium bromide.
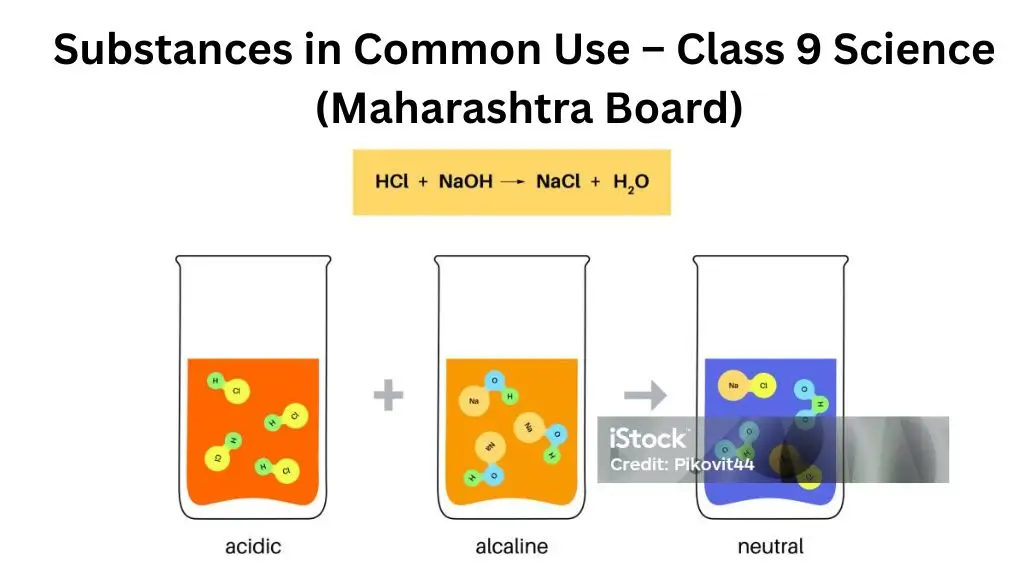
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How is it determined whether a substance is acidic, basic or neutral?
Answer:
- In the pH scale, the pH of solutions varies from 0 to 14 in accordance with the strength of the acids or base.
- The pH scale shows different colours at different values of pH. Colour from dark red to yellow or from pH value 0 to 6 indicates the substances are acidic.
- Colour from light blue to violet or from pH value 8 to 14 indicates the substances are basic.
- Green colour or pH value 7 indicates the substances are neutral.
Question 2.
A sweets shop looks attractive because of the colourful sweets displayed there. Which colours are used in these substances?
Answer:
- Food colours and essences are used in sweets to make them colourful and tasty.
- These food colour are in the form of powders, gels and pastes.
- Food colours are natural as well as artificial.
- The food colours prepared from seeds, beetroot, flowers and fruit concentrate are natural.
- Tetrazene, sunset yellow are artificial food colours used extensively.
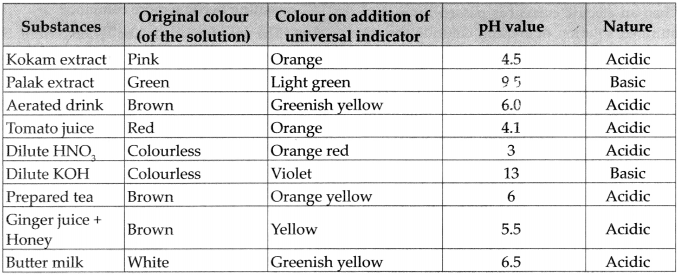
Question 3.
Make a list of substances in day to day use in accordance with their pH value (O to 14).
Answer:
Question 4.
A doctor gives you medicines when you fall ill. What are the medicines made from?
Answer:
Groceries
- Long before pure chemicals were manufactured in labs, people used plants for medicine.
- There are over a hundred active ingredients derived from plants for use as drugs and medicines.
- The emergence of synthetic chemistry in the 1800s opened up new avenues for scientific research into drugs.
- Many chemists tried to locate medically active ingredients in plants (for instance the important malaria remedy quinine), and subsequently tried to make those substances in the laboratory in order to become independent of plant supplies.
- At the same time, a new industry developed as scientists developed processes to synthesise new chemicals on a large scale.
- New production methods developed in the late 1800s and early 1900s made it easier to standardise, package and transport medicines.
Question 5.
What problems do you get after playing colours on Rang Panchami? Why?
Answer:
- After playing colours on Rang Panchami we may get problems such as risks of blindness, skin cancer, asthma, itching of the skin, permanent blocking of sweat pores etc.
- This is because the colours used in rang panchami specially the red colour is very dangerous.
- It contains a high proportion of mercury in it.
Question 6.
Which colours will you use to prevent the occurrence of these problems?
Answer:
- To prevent the occurrence of these problem, instead of using artificial colours, natural colours should be used.
- Natural colours are prepared from natural resouroes such as beet root, flowers of flame of forest, spinach, flame tree (gulmohar).
Question 7.
What problem do you have on painting the house and furniture?
Answer:
- On painting the house and furniture with artificial colours which are dangerous, we may get problems such as risks of blindness, skin cancer, asthma, itching of the skin, permanent blocking of sweat pores, etc.
- This is because the colours contain a high proportion of mercury in it.
Question 8.
What is the property of Teflon because of which it is used in non-stickware?
Answer:
Following are the properties of teflon because of which it is used in nonstick cookware.
- The atmosphere and chemical substances have no effect on Teflon.
- Neither water nor oil will stick to Teflon coated non-stickware.
- High temperatures do not affect Teflon as its melting point is 327 °C.
- Teflon coated non-stickware are easy to clean.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is the strip shown below? What is it used for?
Answer:
The strip shown is pH metre scale. It is used to determined pH of solutions.
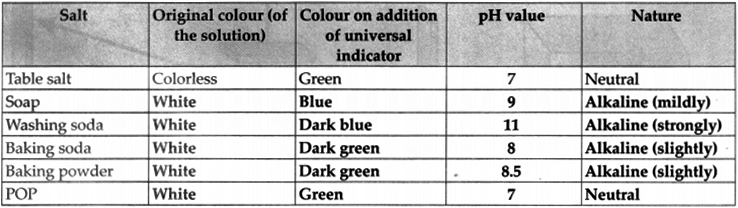
Question 2.
Prepare saturated solutions of given salts and put 2-3 drops of the universal indicator in them and note your observations in the table below:
Answer:
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Substances in Common Use Additional Important Questions and Answers
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Baking soda is used while making cakes.
Answer:
- Baking soda is chemically known as sodium bicarbonate.
- On heating, sodium bicarbonate decomposes to form sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide (CO,).
- The carbon dioxide produced is released due to which the cake becomes soft and spongy.
- Hence, baking soda is used to make cake spongy and soft.
Question 2.
Baking soda is used to reduce acidity in the stomach.
Answer:
- Baking soda is used as a medicine (antacid). When it is taken, it undergoes hydrolysis to give sodium hydroxide in the stomach. Thus, sodium hydroxide neutralizes the hydrochloric acid produced by gastric juice and gives relief to the patient from acidity.
Question 3.
Tap water and water in swimming pool has a typical strong odour in the rainy season.
Answer:
- Tap water and water in swimming pool has a typical strong odour in the rainy season, it is the odour of the chlorine gas that is used to destroy the microbes in the water.
- Chlorine gas is a strong oxidizing agent and therefore, it has a strong disinfecting as well as bleaching action.
- Chlorine is inconvenient to handle because of its gaseous state. Instead, the solid bleaching powder which has the same effect is more convenient to use.
- Bleaching powder undergoes slow decomposition due to the carbon dioxide in air and chlorine gas is released. Bleaching powder gets its property because of this release of chlorine gas.
Question 4.
Sodium carbonate is added to hard water to make it soft.
Answer:
- The hardness of water is due to the presence of chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium in it.
- Na2CO3 is added to it to soften such water and make it suitable for use.
- The reaction with Na2CO3 causes the formation of insoluble carbonate salts of magnesium and calcium thus making the water soft.
Question 5.
Alum is used in the process of water purification.
Answer:
- Alum is used in the process of water purification because of property of coagulation.
- The solid impurities in water come together, become heavy and settle to the bottom.
- As a result, the water above becomes clear.
Question 6.
Overconsumption of artificial food colours should be avoided?
Answer:
Groceries
- The overconsumption of artificial food colours should be avoided because they can be detrimental to health.
- Food colours added to pickles, jam and sauce contain small quantities of lead and mercury. These can be harmful for those who consume these products on a regular basis.
- Diseases like ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) can affect children due to excessive consumption of foods with added food colours.
Question 7.
Artificial colours in Rang Panchami should be used cautiously.
Answer:
- We regularly use artificial colours on Rang Panchami.
- The red colour used on Rang Panchami is very dangerous. It contains a high proportion of mercury in it.
- This poses risks like blindness, skin cancer, asthma, itching of the skin, permanent blocking of sweat pores etc.
- Therefore, it is necessary that artificial colours are used cautiously.
Question 8.
There are various brands of bleaching powder in the market.
Answer:
- When bleaching powder comes in contact with air, it reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate and releases chlorine gas. CaOCl2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + Cl2 ↑ (from air)
- This generated chlorine is known as “available chlorine.”
- On the basis of the percentage of “available chlorine” various brands of bleaching powder are available in the market.
Question 9.
We use anodized cooking utensils like griddles and cookers.
Answer:
Buy vitamins and supplements
- Anodizing is process of forming a protective rayer of hydrated aluminium oxide on utensils.
- Due to anodizing, the surface of the cooking utensils become non-standing, non-toxic and non-reactive with the ingredients of the foot.
- These utensils get heated faster and withstand high heat.
- Also the amount of butter, ghee or oil used to cook food in these type of utensils is neglible.
- These utensils are tough, durable and resistant to corrosion.
- Hence, we use anodized cooking utensils like gridders and cookers.
Explain the following chemical reactions with the help of balanced equations :
Question 1.
Sodium hydroxide reacts with dilute Hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When Sodium hydroxide reacts with dilute Hydrochloric acid, it forms sodium chloride and water.
This is a neutralization reaction.
Question 2.
When an electric current is passed through a saturated solution of sodium chloride (brine)
Answer:
When an electric current is passed through a saturated solution of sodium chloride (brine) it is electrolysed and hydrogen gas is released at the cathode while chlorine gas is released at the anode. Also, an important basic compound NaOH is formed in the cell.
Question Differentiate the following.
Washing soda and Baking soda
Answer:
| Washing soda | Baking soda |
| (i) Chemical name is sodium carbonate. | (i) Chemical name is sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate. |
| (ii) Its molecular formula is Na2CO3.10H2O | (ii) Its molecular formula is NaHCO3 |
| (iii) It is a crystalline substance. | (iii) It is an amorphous powder. |
| (iv) It is used in manufacturing soaps and detergents. | (iv) It is used in bakery for making cakes and bread lighter and spongy. |
Question 8.
What are the adverse effects of dyes?
Answer:
Adverse effects dyes :
- Dyeing hair can have adverse effects like hair fall, damage to hair texture, burning of skin, adverse effect on eyes, etc.
- Lipstick contains a dye named carmine. It does not affect lips but causes stomach disorders.
- Excessive use of plants for making natural dyes results in deterioration of the environment.
Question 9.
Give the uses of teflon.
Answer:
Uses of teflon :
- Teflon is a poor conductor of electricity. Therefore, Teflon clad wires and parts are used in high technology electronic instruments.
- It is used for making non-stick kitchenware.
- The coloured metal sheets of two-wheelers and four-wheelers are given a Teflon coating to protect them from damage due to high temperature and rain.
Question 10.
What is ceramic? Give examples.
Answer:
- Ceramic is a heat resistant substance formed by kneading an inorganic substance in water and then shaping it and hardening it by heating.
- Pots made by a potter, Mangalore roofing tiles, construction bricks, pottery, terracotta articles are some examples of common ceramic articles that we see around.
Question 11.
Give the uses of ceramics.
Answer:
- Ceramics can withstand high temperatures without decomposing. Ceramic is brittle, water-resistant and an electrical insulator.
- Therefore, it is used in electrical instruments, for coating the interior of a kiln, the outer surfaces of ships and blades of jet engines.
- A certain type of ceramic tiles are fixed on the outer layer of a space shuttle. Some types of ceramics are used as superconductors.
❓ IMPORTANT QUESTION & ANSWERS
Q1. What are substances?
Answer:
Substances are materials having a fixed composition and specific properties, used for various purposes in daily life.
Q2. Give examples of substances in common use.
Answer:
Iron, aluminium, copper, plastic, glass, petrol, diesel, LPG, cement, rubber.
Q3. Why are alloys used instead of pure metals?
Answer:
Alloys are stronger, more durable, corrosion-resistant and have better properties than pure metals.
Q4. What are polymers? Give examples.
Answer:
Polymers are long chain molecules made from small units.
Examples: Plastic, nylon, PVC, polythene.
Q5. Name different fuels used in daily life.
Answer:
Coal, petrol, diesel, LPG, CNG, biogas.
🧠 MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions)
1️⃣ Which of the following is a metal?
A) Plastic
B) Glass
C) Iron ✅
D) Rubber
2️⃣ Which substance is used for making electrical wires?
A) Aluminium
B) Copper ✅
C) Iron
D) Zinc
3️⃣ LPG is an example of:
A) Solid fuel
B) Liquid fuel
C) Gaseous fuel ✅
D) Nuclear fuel
4️⃣ Which material is corrosion resistant?
A) Iron
B) Copper
C) Aluminium ✅
D) Zinc
5️⃣ Which is a synthetic polymer?
A) Cotton
B) Wool
C) Nylon ✅
D) Jute
⚡ FQZ – FAST QUIZ (1-Line Answers)
- Iron is used mainly for → Construction
- Plastic is a → Polymer
- Best conductor of electricity → Copper
- Fuel used in vehicles → Petrol/Diesel
- Transparent solid material → Glass
📌 VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Name one alloy → Steel
- One gaseous fuel → CNG
- Non-metal used in daily life → Sulphur
- Material used to make utensils → Aluminium
📊 EXAM ORIENTED POINTS
✔ Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity
✔ Plastics are lightweight and corrosion resistant
✔ Fuels provide energy for transport and industries
✔ Alloys improve strength and durability
❓ FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
FAQ 1. Is Chapter 14 important for exam?
✔ Yes, MCQs and short answers are frequently asked.
FAQ 2. Is this chapter chemistry based?
✔ Yes, it mainly belongs to Chemistry.
FAQ 3. Which topic is most important?
✔ Fuels, polymers, and metals uses.
FAQ 4. Are MCQs asked from this chapter?
✔ Yes, especially in objective exams.