Table of Contents
english grammar class 10
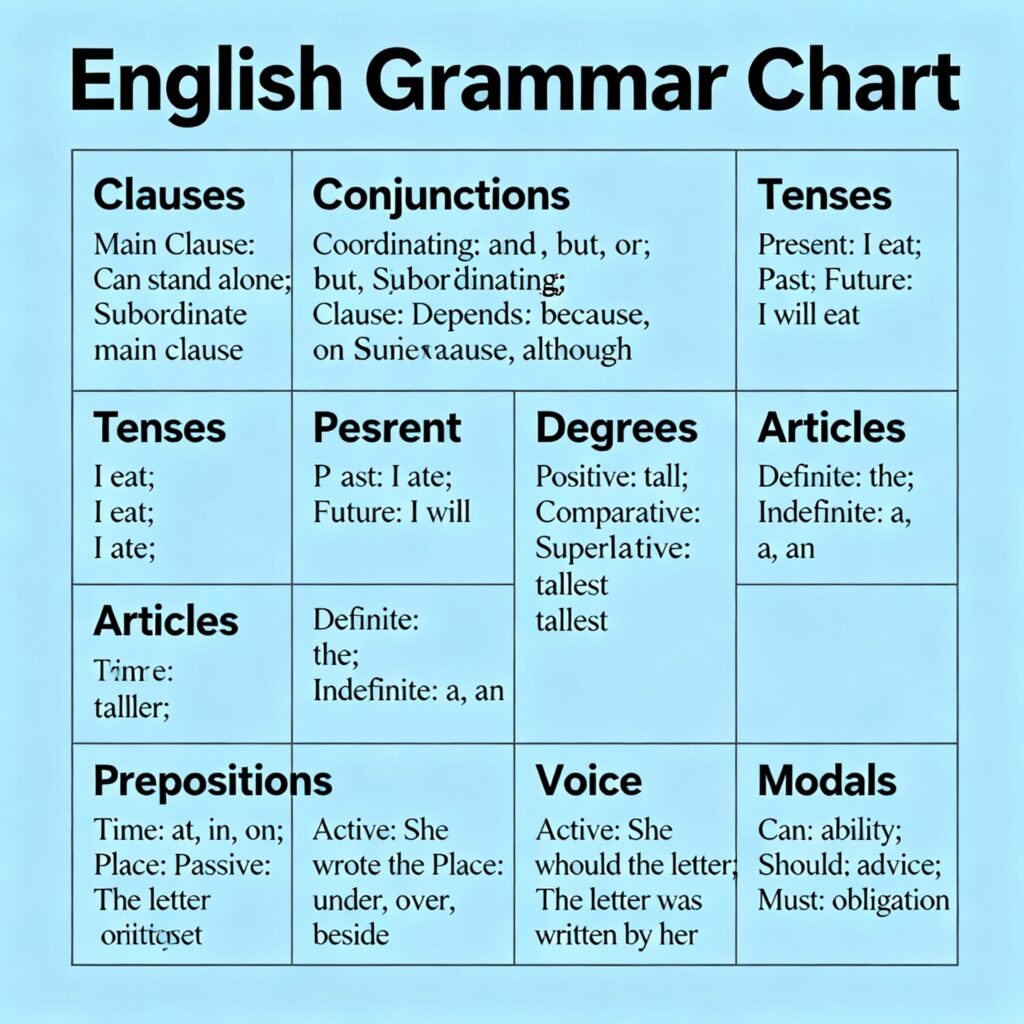
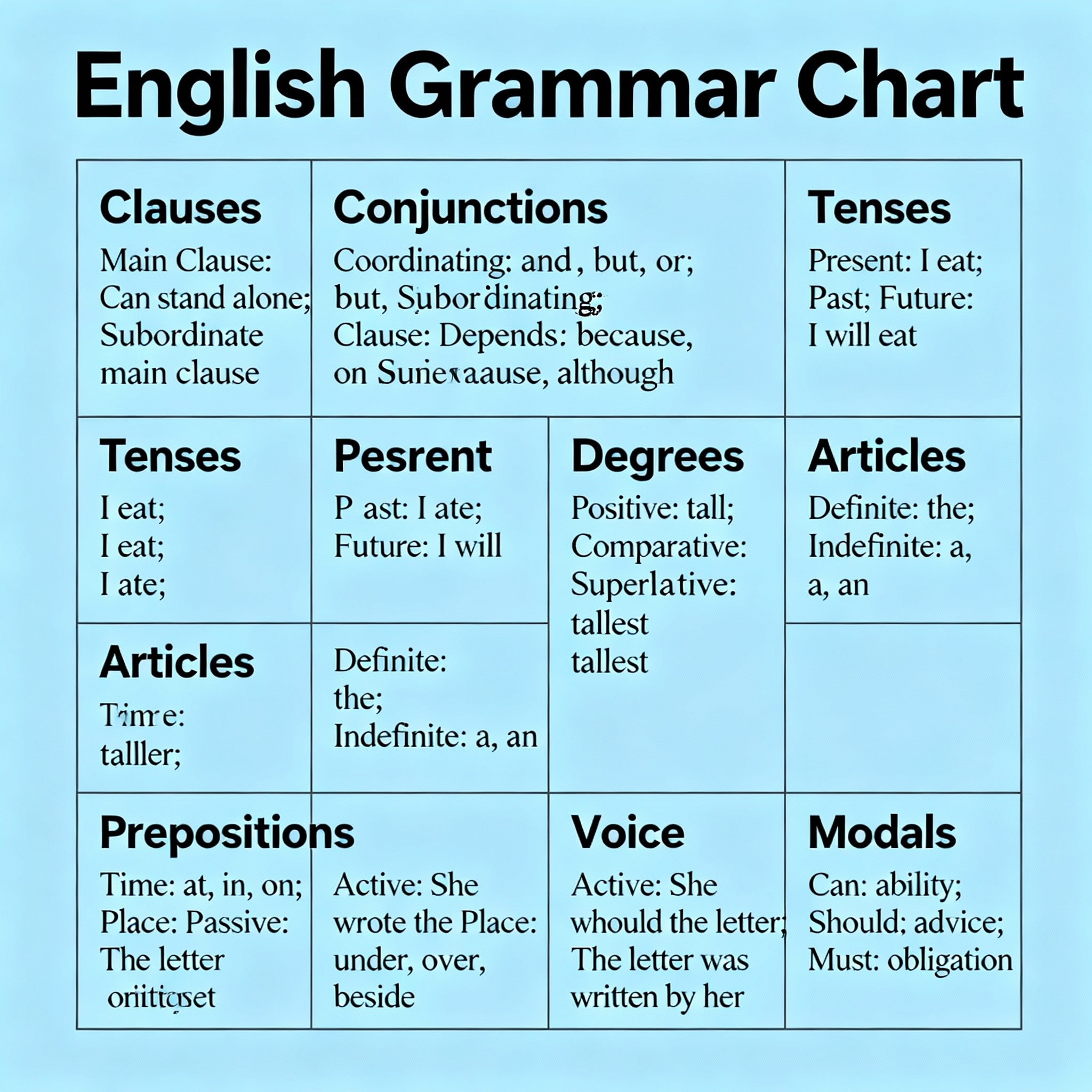
✨ 1. Tenses (काल)
Tense अंग्रेज़ी भाषा का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है। यह हमें बताता है कि कोई कार्य कब हुआ, हो रहा है, या होगा। मुख्य रूप से Tense तीन प्रकार के होते हैं – Present, Past और Future। हर tense के चार sub-types होते हैं – Simple, Continuous, Perfect और Perfect Continuous।
Present Tense
- Simple Present: आदतें, सत्य या Universal fact के लिए।
- Example: The sun rises in the east.
- Present Continuous: इस समय चल रहे कार्य के लिए।
- Example: I am writing a letter.
- Present Perfect: कार्य हाल ही में पूरा हो चुका है और असर अब तक है।
- Example: He has completed his homework.
- Present Perfect Continuous: अतीत से अब तक जारी कार्य के लिए।
- Example: They have been playing since morning.
Past Tense
- Simple Past: अतीत में हुआ कार्य।
- Example: She visited Delhi last year.
- Past Continuous: अतीत में चल रहा कार्य।
- Example: I was reading when he came.
- Past Perfect: किसी दूसरे past action से पहले का कार्य।
- Example: He had left before I reached.
- Past Perfect Continuous: अतीत से लगातार चल रहा कार्य।
- Example: She had been working for two hours.
Future Tense
- Simple Future: भविष्य में होने वाला कार्य।
- Example: I will go to market tomorrow.
- Future Continuous: भविष्य में चल रहा कार्य।
- Example: She will be studying at 8 p.m.
- Future Perfect: भविष्य में एक निश्चित समय तक कार्य पूरा हो जाएगा।
- Example: They will have finished the work by 5 p.m.
- Future Perfect Continuous: भविष्य में एक निश्चित समय तक चलता रहने वाला कार्य।
- Example: He will have been working here for 10 years next month.
📌 Practice:
- She ___ (read) a book now.
- By next year, I ___ (complete) my studies.

✨ 2. Articles (A, An, The)
Articles English grammar में nouns से पहले आते हैं और उनका nature बताते हैं। Articles दो प्रकार के होते हैं: Definite (The) और Indefinite (A, An)।
- A: consonant sound से पहले प्रयोग (a boy, a pen, a university – यहाँ university ‘yu’ sound से शुरू है)।
- An: vowel sound (a, e, i, o, u) से पहले प्रयोग (an apple, an honest man – यहाँ honest में ‘h’ silent है)।
- The: specific noun के लिए प्रयोग (the sun, the Taj Mahal, the Ganga)।
Rules:
- Generic nouns के साथ “A/An” – A dog is a faithful animal.
- Unique nouns के साथ हमेशा “The” – The Moon, The Earth.
- Superlative degree के साथ “The” – The tallest boy.
- Musical instruments के साथ – He plays the flute.
📌 Practice:
- She bought ___ book yesterday.
- The moon shines in ___ sky.
✨ 3. Prepositions (पूर्वसर्ग)
Prepositions ऐसे शब्द होते हैं जो noun या pronoun का relation किसी दूसरे word से बताते हैं। ये time, place, direction या reason दिखाते हैं।
Types:
- Preposition of Place: in, on, under, over, between (The book is on the table.)
- Preposition of Time: at, in, on, since, for (I was born in 2005.)
- Preposition of Direction: to, towards, into, onto (She is going to school.)
- Preposition of Cause/Reason: because of, due to (He failed because of laziness.)
Common Errors:
- Incorrect: She is married with him.
- Correct: She is married to him.
📌 Practice:
- The pen is ___ the table.
- He has been living in Delhi ___ 2010.
✨ 4. Active and Passive Voice
Voice बताता है कि sentence का subject काम करता है या उस पर काम होता है।
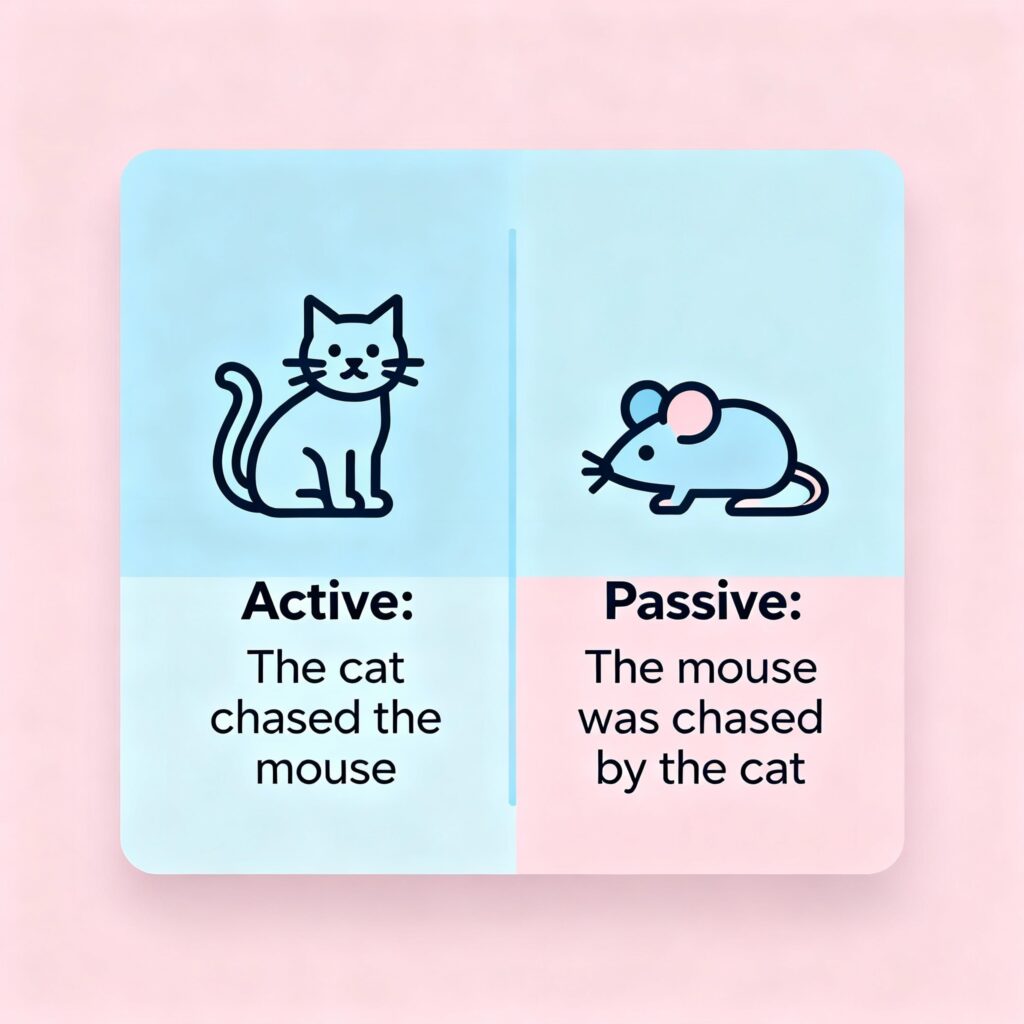
- Active Voice: जब subject खुद action करता है।
- Example: Ram writes a letter.
- Passive Voice: जब subject पर action होता है।
- Example: A letter is written by Ram.
Rules:
- Object → Subject बन जाता है।
- Verb का रूप बदलता है → be verb + V3.
- Subject → by + Object बन जाता है।
📌 Example:
- Active: The teacher teaches English.
- Passive: English is taught by the teacher.
📌 Practice:
- She sings a song. (Passive में बदलिए)
- They are playing cricket. (Passive में बदलिए)
✨ 5. Direct and Indirect Speech
जब हम किसी के exact words को quote करते हैं तो उसे Direct Speech कहते हैं। जब उन्हीं words को report करते हैं तो वह Indirect Speech कहलाता है।
Example:
- Direct: He said, “I am happy.”
- Indirect: He said that he was happy.
Rules:
- Present → Past (I am → He was)
- Tomorrow → The next day
- Today → That day
- Will → Would
📌 Practice:
- He said, “I will come tomorrow.”
- She said, “I am reading a book.”
✨ 6. Modals
Modals auxiliary verbs हैं जो ability, possibility, necessity, advice, permission आदि दर्शाते हैं।
Common Modals:
- Can (ability): I can swim.
- Could (past ability): He could run fast.
- May (permission): May I come in?
- Must (necessity): You must work hard.
- Should (advice): You should respect elders.
- Might (possibility): It might rain today.
📌 Practice:
- You ___ obey your parents. (must/should)
- He ___ run fast when he was young. (can/could)
1. Clauses (उपवाक्य)
परिभाषा:
Clause वह समूह होता है जिसमें subject और verb दोनों होते हैं, परंतु वह अपने आप पूरा अर्थ नहीं दे सकता। Clause sentence का हिस्सा होता है।
प्रकार:
- Noun Clause (संज्ञा उपवाक्य):
यह वाक्य में noun की तरह काम करता है।- Example: I know that she is honest.
- यहाँ पूरा highlighted भाग noun की तरह “object” है।
- Adjective Clause (विशेषण उपवाक्य):
यह किसी noun या pronoun की विशेषता बताता है।- Example: This is the boy who won the prize.
- यहाँ clause “boy” को qualify कर रहा है।
- Adverb Clause (क्रिया विशेषण उपवाक्य):
यह verb को modify करता है और reason, time, place आदि बताता है।- Example: He ran fast because he was late.
महत्व:
Clauses से complex sentences बनते हैं, जो भाषा को समृद्ध और स्पष्ट बनाते हैं।
📌 Practice:
- Identify the clause – “I believe that he is right.”
- Join using clause – This is the place. We met here.
✨ 2. Conjunctions (समुच्चयबोधक अव्यय)
परिभाषा:
Conjunction वे शब्द होते हैं जो दो शब्द, phrases या clauses को जोड़ते हैं।
प्रकार:
- Coordinating Conjunctions:
समान महत्त्व वाले शब्द या clauses को जोड़ते हैं।- Example: and, but, or, nor, yet, for, so
- I like tea and coffee.
- Subordinating Conjunctions:
एक main clause और एक subordinate clause को जोड़ते हैं।- Example: because, although, if, since, when, unless
- I stayed home because it was raining.
- Correlative Conjunctions:
ये जोड़े में प्रयोग होते हैं।- Example: either…or, neither…nor, both…and, not only…but also
- She is not only beautiful but also intelligent.
Common Errors:
- Incorrect: Either he will come or not.
- Correct: Either he will come or he will not.
📌 Practice:
- He is poor ___ he is honest. (but/because)
- You can take ___ tea ___ coffee. (either/or)
✨ 3. Transformation of Sentences (वाक्य रूपांतरण)
परिभाषा:
Transformation का अर्थ है एक sentence को दूसरे रूप में बदलना, परंतु उसका अर्थ वही रखना। यह Grammar का महत्वपूर्ण भाग है।
मुख्य प्रकार:
- Affirmative ↔ Negative
- She is intelligent. → She is not unintelligent.
- Simple ↔ Complex ↔ Compound
- Simple: He is too weak to walk.
- Complex: He is so weak that he cannot walk.
- Compound: He is weak, and he cannot walk.
- Active ↔ Passive Voice
- Active: Ram wrote a letter.
- Passive: A letter was written by Ram.
- Direct ↔ Indirect Speech
- Direct: She said, “I am tired.”
- Indirect: She said that she was tired.
- Exclamatory ↔ Assertive
- How beautiful the flower is! → The flower is very beautiful.
महत्व:
यह skill विद्यार्थियों को विभिन्न exam questions में मदद करता है क्योंकि transformation से sentence structure clear होता है।
📌 Practice:
- Change to negative: He is a good boy.
- Change to complex: She is too weak to run

✨ 4. Degrees of Comparison (तुलना के भेद)
परिभाषा:
Adjectives की तीन forms होती हैं जिन्हें Degrees of Comparison कहते हैं।
प्रकार:
- Positive Degree:
adjective का साधारण रूप।- Example: She is a tall girl.
- Comparative Degree:
दो व्यक्तियों/वस्तुओं की तुलना के लिए।- Example: She is taller than her sister.
- Superlative Degree:
तीन या अधिक की तुलना में सर्वोच्च रूप।- Example: She is the tallest girl in the class.
Rules:
- One-syllable adjectives में “-er/-est” जोड़ते हैं (tall → taller → tallest)।
- Two या अधिक syllables वाले adjectives में “more/most” लगाते हैं (beautiful → more beautiful → most beautiful)।
- Irregular adjectives – good → better → best; bad → worse → worst।
Common Errors:
- Incorrect: She is more taller than her sister.
- Correct: She is taller than her sister.
📌 Practice:
- Positive → Comparative: This book is interesting.
- Comparative → Superlative: Ram is stronger than Mohan.
English Grammar Practice (With Answers)
✨ 1. Clauses (उपवाक्य)
Questions:
- Identify the noun clause: I know that he is honest.
- Identify the adjective clause: This is the boy who won the prize.
- Identify the adverb clause: He went home because he was tired.
- Combine: She met a man. He was a doctor.
- Make complex: He is too weak to walk.
- Find the clause: I don’t know where she lives.
- Combine: I saw a girl. She was singing.
- Change into complex: On his arrival, we started our work.
- Identify: I believe that honesty is the best policy.
- Rewrite: This is the place where we met.
Answers:
- that he is honest → Noun clause
- who won the prize → Adjective clause
- because he was tired → Adverb clause
- She met a man who was a doctor.
- He is so weak that he cannot walk.
- where she lives → Noun clause
- I saw a girl who was singing.
- When he arrived, we started our work.
- that honesty is the best policy → Noun clause
- where we met → Adjective clause
✨ 2. Conjunctions (समुच्चयबोधक)
Questions:
- He is poor ___ he is honest.
- She is beautiful ___ intelligent.
- You can take ___ tea ___ coffee.
- I worked hard ___ I failed.
- He ran fast ___ he missed the train.
- Neither he ___ his brother was present.
- ___ he was tired, he kept working.
- He cannot succeed ___ he works hard.
- I like cricket ___ football.
- Correct: Either he will come or not.
Answers:
- but
- and
- either/or
- yet
- but
- nor
- Although
- unless
- and
- Either he will come or he will not.
✨ 3. Transformation of Sentences
Questions:
- Change into negative: She is honest.
- Change into passive: Ram writes a letter.
- Change into indirect: He said, “I am happy.”
- Change into exclamatory: The weather is very beautiful.
- Change into simple: As soon as the bell rang, the students left.
- Change into complex: He is too poor to buy a car.
- Change into compound: He is so weak that he cannot run.
- Change to affirmative: She is not dishonest.
- Change into passive: They are playing cricket.
- Change into direct: He said that he was tired.
Answers:
- She is not dishonest.
- A letter is written by Ram.
- He said that he was happy.
- How beautiful the weather is!
- On the ringing of the bell, the students left.
- He is so poor that he cannot buy a car.
- He is weak, and he cannot run.
- She is honest.
- Cricket is being played by them.
- He said, “I am tired.”
✨ 4. Degrees of Comparison
Questions:
- Positive: This book is interesting. (Comparative?)
- Comparative: She is taller than her sister. (Superlative?)
- Superlative: Mount Everest is the highest peak. (Positive?)
- Rewrite: He is better than any other player. (Superlative)
- Rewrite: She is as tall as her brother. (Comparative)
- Correct: He is more wiser than me.
- Change: The Ganga is the holiest river. (Comparative)
- Rewrite: She is one of the most intelligent girls. (Positive)
- Rewrite: Iron is stronger than wood. (Positive)
- Rewrite: No other city is as big as Delhi. (Superlative)
Answers:
- This book is more interesting than that one.
- She is the tallest girl.
- No other peak is as high as Mount Everest.
- He is the best player.
- She is not taller than her brother.
- He is wiser than me.
- The Ganga is holier than any other river.
- Very few girls are as intelligent as she is.
- Wood is not as strong as iron.
- Delhi is the biggest city.
✨ 5. Tenses (काल)
Questions:
- She ___ (go) to school daily. (Simple Present)
- I ___ (read) a book now. (Present Continuous)
- He ___ (finish) his homework. (Present Perfect)
- They ___ (play) since morning. (Present Perfect Continuous)
- She ___ (visit) Delhi last year. (Simple Past)
- I ___ (read) when he came. (Past Continuous)
- He ___ (leave) before I reached. (Past Perfect)
- She ___ (work) for two hours. (Past Perfect Continuous)
- I ___ (go) to market tomorrow. (Simple Future)
- They ___ (complete) the work by 5 p.m. (Future Perfect)
Answers:
- goes
- am reading
- has finished
- have been playing
- visited
- was reading
- had left
- had been working
- will go
- will have completed
✨ 6. Articles (A, An, The)
Questions:
- She bought ___ pen.
- He saw ___ honest man.
- There is ___ apple on the table.
- ___ Sun rises in the east.
- He is ___ university student.
- This is ___ Taj Mahal.
- She is ___ European lady.
- I met ___ MLA yesterday.
- He plays ___ guitar.
- She read ___ Bible.
Answers:
- a
- an
- an
- The
- a
- the
- a
- an
- the
- the
✨ 7. Prepositions (पूर्वसर्ग)
Questions:
- The book is ___ the table.
- She lives ___ Delhi.
- He was born ___ 2005.
- The cat is hiding ___ the bed.
- The boy is sitting ___ the chair.
- He is good ___ English.
- I will meet you ___ Monday.
- She jumped ___ the river.
- He walked ___ the park.
- This gift is ___ you.
Answers:
- on
- in
- in
- under
- on
- at
- on
- into
- through
- for
✨ 8. Active and Passive Voice
Questions:
- Ram writes a letter. (Passive)
- She is cooking food. (Passive)
- They have completed the work. (Passive)
- He was writing a story. (Passive)
- She will help me. (Passive)
- Who wrote this book? (Passive)
- The teacher teaches us English. (Passive)
- The police caught the thief. (Passive)
- They are watching a movie. (Passive)
- The king built a palace. (Passive)
Answers:
- A letter is written by Ram.
- Food is being cooked by her.
- The work has been completed by them.
- A story was being written by him.
- I will be helped by her.
- By whom was this book written?
- We are taught English by the teacher.
- The thief was caught by the police.
- A movie is being watched by them.
- A palace was built by the king.
✨ 9. Modals
Questions:
- He ___ swim. (ability)
- You ___ work hard. (necessity)
- ___ I come in? (permission)
- It ___ rain today. (possibility)
- We ___ respect our elders. (advice)
- He ___ run fast when he was young. (past ability)
- You ___ not smoke here. (prohibition)
- She ___ be at home now. (guess)
- Students ___ wear uniform. (obligation)
- He ___ win the match if he tries. (possibility)
Answers:
- can
- must
- May
- might
- should
- could
- must
- may
- must
- can
FAQs on English Grammar (with Hindi Explanation)
Q1. What are Clauses in English Grammar? (क्लॉज़ क्या होते हैं?)
Answer:
A clause is a group of words that has a subject and a verb and makes complete sense or part of a sentence.
👉 Example: I know that he is honest. (यहाँ “that he is honest” एक clause है।)
Q2. What are Conjunctions? (Conjunctions क्या हैं?)
Answer:
Conjunctions are joining words used to connect words, phrases, or sentences.
👉 Example: She is poor but honest. (but = conjunction)
Q3. What is Transformation of Sentences?
Answer:
Transformation of sentences means changing the form of a sentence without changing its meaning.
👉 Example: She is very beautiful. → How beautiful she is!
Q4. What are Degrees of Comparison? (Degree क्या है?)
Answer:
Degrees of Comparison show comparison between adjectives.
- Positive: Ram is tall.
- Comparative: Ram is taller than Shyam.
- Superlative: Ram is the tallest boy in the class.
Q5. How many types of Tenses are there? (Tense कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?)
Answer:
There are 3 main tenses: Present, Past, Future.
Each has 4 forms → Simple, Continuous, Perfect, Perfect Continuous.
👉 Total = 12 Tenses.
Q6. What are Articles in English Grammar? (Articles क्या होते हैं?)
Answer:
Articles are words (A, An, The) used before nouns.
- A/An = Indefinite Article
- The = Definite Article
👉 Example: She bought a book. / The sun rises in the east.
Q7. What are Prepositions? (Prepositions क्या हैं?)
Answer:
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to show relation with another word.
👉 Example: The book is on the table. (on = preposition)
Q8. What is Active and Passive Voice?
Answer:
- Active Voice: Subject does the action.
👉 Example: The teacher teaches English. - Passive Voice: Subject receives the action.
👉 Example: English is taught by the teacher.
Q9. What are Modals in English Grammar?
Answer:
Modals are helping verbs used to express possibility, necessity, permission, or ability.
👉 Examples: can, could, may, might, shall, should, must, will, would.
👉 Example: You must work hard.
Q10. Why are these grammar topics important for Class 6–10 and Competitive Exams?
Answer:
Because they form the base of English language learning. All exams (Board + Competitive) have grammar sections based on these topics. Good command improves writing, speaking, and comprehension skills.








[…] Read : English Grammar Class 10 […]