Table of Contents
Part 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms 9th Science Notes

1. Match the pairs and explain.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Growth of pollen tube towards ovules (2) Growth of shoot system (3) Growth of root system (4) Growth towards the water | (a) Gravitropic movement (b) Chemotropic movement (c) Phototropic movement (d) Growth-irrelevant movement (e) Hydrotropic movement |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a),
(4 – e).
2. Complete the paragraph.
The milk was on the stove. Rasika was engrossed in watching television. She smelled something burning. She ran towards the kitchen. The milk was boiling over. She held the vessel with her bare hands but, screaming, she let it go at once. This activity was controlled by ……………….. cells. Special ends of ……………….. in these cells collected the information, from where it was transferred to the ……………….. and then towards the terminal end of the ……………….. The chemicals produced at the terminal end passed through the minute space i.e. ………………. . In this way, ……………….. were conducted in the body and the process of ……………….. was completed by conducting the impulses from ……………….. to ………………
(Nerve, muscle cell, impulse, dendrite, synapse, axon, reflex action, cell body)
Answer:
nerve, dendrite, cell body, axon, synapse, impulses, reflex action, nerve, muscle cell.
3. Write notes on Root pressure, Transpiration, Nerve cell, Human brain, Reflex action
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Root Pressure
Answer:
- Root cells are in contact with water and minerals in the soil.
- Water and minerals enter the cells of the root surface due to difference in concentration. As a result, these cells become turgid.
- This is called root pressure.
- Under the effect of this pressure, water and minerals reach the xylem of the roots and to reduce this difference in concentration, they are continuously pushed forward.
- As a result of this continuous movement, a water column is formed, which is continuously pushed ahead.
- This pressure, is sufficient to lift the water up in shrubs, small plants and small trees.
Question 2.
Transpiration
Answer:
- Plants give out water in the form of water vapour through the stomata on their leaves. This is known as transpiration.
- Two cells called guard cells are present around the stomata. They control the opening and closing of stomata.
- Water is released into the atmosphere by leaves through the process of evaporation.
- As a result, water in the epidermal layer of the leaf decreases.
- Water is brought up to the leaves through the xylem to compensate for the lost water.
- Transpiration helps in absorption of water and minerals and distribution to all parts of the plant.
Question 3.
Read : Part 12 Study of Sound 9th Science Notes
9th Science Notes Maharashtra Board Part 11
Nerve cell
Answer:
- Nerve cells also called as neurons are special types of cells which conduct impulses from one place to another in the body.
- Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system.
- Nerve cells, the largest cell in the human body, may measure upto a few metres in length.
- Nerve cells have the ability to generate and conduct electrochemical impulse.
- The cells that support the nerve cells and help in their functioning are called neuroglia. Nerve cells and neuroglial cells together form nerves.
Question 4.
Reflex action
Answer:
- An immediate and involuntary response given to a stimulus from the environment is called a reflex action.
- Sometimes we react to an incident without any thinking on our part or control over the reaction.
- This is a response given to a certain stimulus from the surroundings.
- In such situations, proper control and co-ordination is achieved even without the intervention of the brain.
- For example, when our hand touches a hot object, the receptor in the skin detects the stimulus.
- The sensory neuron sends the impulse to the relay neuron in the spinal cord.
- The impulses are then sent to motor neurons which cause the muscles of the hand to contract and move away from the hot object.
- The spinal cord is the center of co-ordination for reflex actions.
Human Brain
Answer:
- The brain is the main controlling part of the nervous system and is safely located in the cranial cavity.
- The brain is covered by protective layers called the Meninges.
- Cavities present in various parts of the brain are called ventricles.
- The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid supplies nutrients to the brain and also protects it from shock.
- The brain of an adult human weighs about 1300 -1400 grams and consists of approximately 100 million neurons.
- The left side of our brain controls the right side of our body and right side of our brain controls left side of the body.
- In addition, the left side of the brain controls our speech and conversation, writing, logical thinking etc., whereas the right side controls artistic abilities.
Human brain is made up of following parts:
(a) Cerebrum:
- This is the largest part of the brain and consists of two cerebral hemispheres. These hemispheres are joined with each other with the help of tough fibres and nerve tracts.
- The cerebrum occupies two-thirds of the brain. Hence, it is also called as large brain.
- Its surface has deep, irregular ridges and grooves which are called convolutions, convolution increases the surface area of the cerebrum and therefore a large number of nerve cells can be accommodated.
(b) Cerebellum:
- This is the smaller part of the brain situated below the cerebrum at the back of the cranial cavity.
- Its surface shows shallow grooves instead of deep convolutions.
(c) Medulla Oblongata:
- This is the hind-most part of the brain.
- There are two triangular swollen structures called pyramids on the upper side of medulla oblongata.
- The medulla oblongata continues downwards the spinal cord.
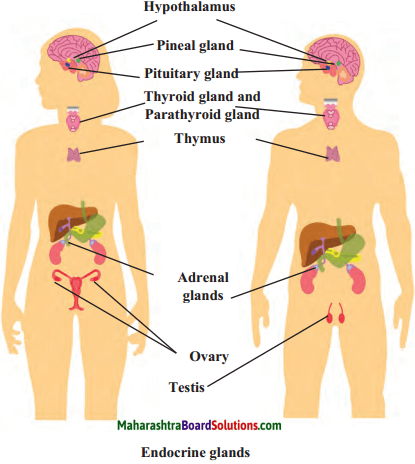
4. Name the hormones of the following endocrine glands and the function of each.
Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenal, Thymus, Testis, Ovary.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Question 1.
Pituitary:
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Growth hormone | Stimulates growth of bones. |
| (ii) Adrenocorticotropic hormone | Stimulates adrenal gland. |
| (iii) Thyroid-stimulating hormone | Stimulates thyroid gland. |
| (iv) Prolactin | Stimulates milk production. |
| (v) Follicle-stimulating hormone | Controls growth of gonads. |
| (vi) Luteinizing hormone | Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation. |
| (vii) Oxytocin | Contracts uterus during parturition. |
| (viii) Antidiuretic hormone | Regulates water-level in the body. |
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 2.
Thyroid
Answer:
| Hormone | Function | |
| (i) Thyroxine | Controls growth of body and metabolic activities. | |
| (ii) Calcitonin | Controls calcium metabolism and calcium level in blood. | |
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Exercise Question 3.
Adrenal
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Adrenalin and nor-adrenalin | Controls behaviour during crisis and emotional situation. |
| (ii) Corticosteroid | Maintains balance of Na+ and K+ and stimulates metabolism. |
Thymus
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| Thymosin | Control the cells which give rise to immunity. |
Question 5.
Testis
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| Testosterone | Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics like beard, mustache, hoarse voice etc. in men. |
Ovary
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Oestrogen | Stimulates growth of the endometrium. Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics in women. |
| (ii) Progesterone | Prepares the endometrium for conception and maintains pregnancy. |
5. Draw and label the diagrams.
Human endocrine glands, Human brain, Nephron, Nerve cell, Human excretory system.
15. Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 1.
Human endocrine glands
Answer:
Human brain
Answer:
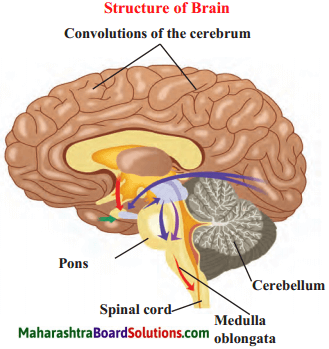
Nephron
Answer:
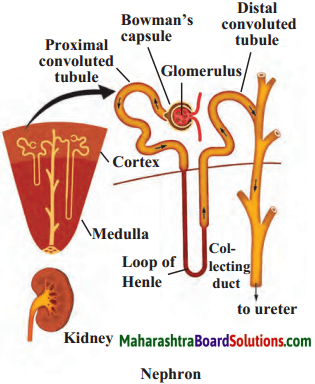
Nerve cell
Answer:
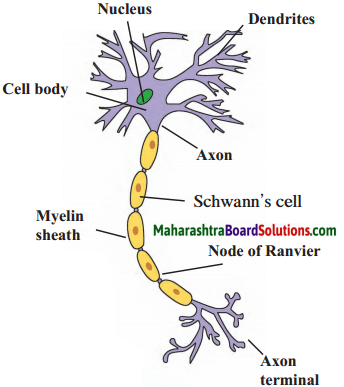
Human excretory system
Answer:
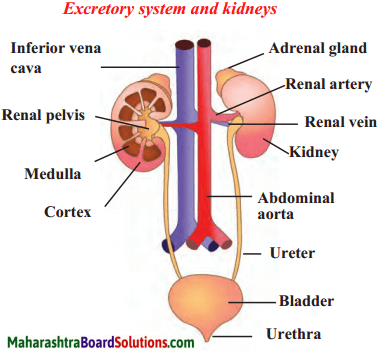
6. Answer the following.
a. Explain chemical co-ordination in humans and give the names and functions of some hormones.
Answer:
Chemical co-ordination in humans :
- In humans chemical co-ordination is brought about with the help of certain chemical substances called hormones.
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands. These glands are also called ductless glands.
- These glands do not have any arrangement of their own to either store or carry their secretions. So, the hormones are directly released into the blood circulation.
- Though the endocrine glands are present at specific locations in our body, their secretions reach all parts of the body via the blood.
- Endocrine glands along with the nervous systems are responsible for control and co-ordination in our body.
These two systems help each other to control and integrate the various activities of the body. - A marked difference between these two systems is that nerve impulses are fast but short-lived whereas the actions of hormones are very slow but long-lasting.
- It is very important that hormones are secreted only in the required quantity and there is a special mechanism which controls the quantity and timing of hormone secretion.
- For example, whenever there is an increase in blood glucose level, certain cells in the pancreas get stimulated and as a response, they release a greater quantity of insulin, thus bringing down the sugar level to normal.
| Hormone | Function |
| (1) Growth hormone | Stimulates growth of bones. |
| (2) Luteinizing hormone | Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation. |
| (3) Thyroxine | Controls growth of body and metabolic activities. |
| (4) Insulin | Stimulates liver to convert excess blood glucose to glycogen. |
| (5) Testosterone | Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characters like beard, mustache, hoarse voice, etc. in men. |
Names and functions of some hormones:
b. Explain the difference between the excretory system of humans and plants.
Answer:
| Excretory system of humans | Excretory system of plants |
| (i) In humans, the excretory system carries out the function of the removal of waste from the body. | (i) In plants, there is no special system or organ for excretion. |
| (ii) Waste substances are generally eliminated out of the body | (ii) Most of the waste substances are stored in the leaves, flowers, fruits and bark of the stem. |
| (iii) The excretory products are urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc. | (iii) The excretory products are gum, resin, latex of rubber, etc. |
c. Explain co-ordination in plants with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
- Plants do not have systems like the nervous system or muscular system.
- In plants, movements are mainly in the form of responses given to the stimuli.
- Plants show two types of movements – growth relevant movements and growth irrelevant movements.
- Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called tropism or tropic movement.
- Examples of growth-relevant movements are :
- The shoot system of any plant responds to the light stimulus i.e., it grows towards the source of light. This is called phototropic movement.
- The root system of plants responds to stimuli like gravitation and water. These responses are called gravitropic movement and hydrotropic movement respectively.
- Movement shown by plants in response to specific chemicals is called chemotropic movement.
- For example, the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule.
- Some specific movements of the plants do not lead to the plant growth.
- Such movements are called growth-irrelevant movements.
- As a response to changes in the surroundings, plant hormones bring about various movements in plants.
- Examples of growth irrelevant movements are closing of leaflets of Touch-me-not (Mimosa) plant on touch.
- In the plant called Venus fly trap, when an insect visits the flower like trap, the trap closes up and the trapped insect is digested by the plant.
- The lotus flower opens during day-time while that of the tuberose opens at night.
- In plants like Touch-me-not (Mimosa), movement also occurs at places other than where it has been touched.
- Hence, we can infer that the information about the touch must have been released within the plant from one place to another.
- Plants use electrochemical impulses for transfer of information from one place to another.
- Plant cells change their shape by increasing or decreasing the water content and thereby, bring about the movements of plants.
Life Processes in Living Organisms class 9th pdf
7. Explain in your own words with suitable examples.
a. What is meant by co-ordination?
Answer:
- Several different organ systems function in multicellular organisms.
- Their life goes on smoothly if there is co-ordination between different organ systems or organs and the stimuli in the surrounding.
- Depending upon this, we can say that systematic regulation of different processes can be called control and bringing about the different processes in the proper sequence is called co-ordination.
- If any activity in the body is to be completed successfully, proper co-ordination between different systems, and organs participating at different steps of that activity is necessary.
- If due to lack of co-ordination, there is confusion at any step, the activity may not get completed. There should be no randomness at any step.
- There should be proper co-ordination between internal activities of the body resulting from various factors like body temperature, water- level, enzyme-level, etc. or stimuli arising in the surrounding environment.
- Proper co-ordination between various systems of an organism helps to maintain a state of equilibrium called homeostasis which is necessary for the optimal efficiency of the body.
b. How does excretion occur in human beings?
Answer:
- Removal of wastes from the body is very important and it is the excretory system that carries out this function.
- The human excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, the urinary bladder and the urethra. Urine is formed by the kidneys by separating the waste and unwanted excess substances from the blood.
- The functional unit of the kidney that performs the basic function of filtration is called a nephron. The urea produced in the liver comes into the blood.
- When the urea-containing blood comes into the glomerulus, it is filtered through capillaries and urea and other similar substances are separated from it.
- Water molecules and small molecules of some other substances can cross the semipermeable membrane of Bowman’s capsule.
- The solution accumulated in the cavity of Bowman’s capsule passes into the tubular part of the nephron. Here, molecules of water and some other useful substances are reabsorbed into the blood.
- Urine is formed from the remaining solution which is full of waste materials. The urine is carried by the ureters and stored in the urinary bladder. Afterwards, urine is given out through the urethra.
c. How is excretion in plants useful to human beings?
Answer:
- Plants give out oxygen during photosynthesis by diffusion which is useful to human beings for respiration.
- Some waste materials of plants for example, gum, resin, latex of rubber, etc. are useful to humans.
d. Describe the transportation system in plants.
Answer:
- Plants have two types of conducting tissues i.e., xylem which conducts water and phloem which conducts food.
- During transpiration, water is released into the atmosphere.
- As a result, water level is the epidermal layer of the leaf decreases.
- Water is brought up to the leaves through the xylem so as to compensate for the lost water.
- Transpiration helps in absorption of water and minerals and distribution to all parts of the plant whereas root pressure preforms the important role of pushing the water up at night time.
- The food produced by leaves is transported to each cell of the plant through phloem.
- When the food material like sucrose is transported towards a part of the plant through phloem, using ATP, the water concentration in that part decreases.
- As a result, water enters the cell by diffusion. The pressure on the cell wall increases due to increase in the cellular contents.
- Due to the increased pressure, food is pushed into the neighboring cells where the pressure is low.
- This process helps the phloem to transport the materials as per the need of the plant.
Extra Question : Life Processes in Living Organisms class 9th notes pdf donwload
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 1.
How do the digestive system and respiratory system work?
Answer:
(1) Digestive system:
- The digestive system is responsible for digestion of food. i.e. breaking down complex insoluble food into simpler soluble form.
- The digestive system is made up of alimentary canal and digestive glands.
- The alimentary canal is a long and muscular tube of varying diameter which extends from the mouth to the anus.
- The digestive glands associated with alimentary canal are salivary glands, gastric glands, liver and pancreas.
- The process of digestion includes various stages wherein the food passes through the different organs of the alimentary canal and there it is digested part by part with the help of various enzymes secreted from the digestive glands.
- After the food is digested, the important nutrients are absorbed into the blood and the undigested food and residue of digested food is removed out of the body through the anus.
(2) Respiratory system:
- Respiration is the process of release of energy from the assimilated food.
- The respiratory system consists of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs (alveoli).
- Oxygen enters our body through breathing.
- This oxygen is taken to the cells and with the help of oxygen, food is oxidized into the cells to release energy in the form of ATR
- During this process, carbon dioxide and water vapour are given out as by-products which are given out during breathing.
Thus, the digestive and respiratory systems work in co-ordination with each other to produce energy from food.
Life Process In Living Organism Exercise Question 3.
(3) Which are the sensory organs of an organism? What is their function?
Answer:
- Sensory organs of an organism are eyes, ears, tongue, skin and nose.
- The eyes help the organism to perceive the sensation of light to see the objects around it.
- The ears help the organism to perceive the sensation of sound and also perceive the sensation of pressure.
- The tongue helps to perceive different tastes and also in chewing the food.
- The skin helps to perceive the sensation of touch, pain, pressure etc.
- Some insects also possess antennae for sensing the changes in the environment.
9th Class Science 15 Chapter Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 5.
(4) Sometimes, we choke while eating in a hurry.
Answer:
- There is an elastic flap at the starting of the wind-pipe called epiglottis which opens whenever we breathe in air and closes to prevent the entry of food into the respiratory system.
- While eating in hurry, due to lack of co-ordination, the epiglottis opens to take in air but food too enters in causing us to choke.
15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 9.
Which waste products are produced in our body through metabolic activities?
Answer:
The waste products formed in our body through metabolic activities are urea, uric acid, ammonia, carbon dioxide etc.
Give scientific reasons: 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms class 9th
(5) It is necessary to remove harmful and waste substances from the body.
Answer:
- Many harmful and waste substances like urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc. are produced in living organisms.
- If these substances accumulate in the body or are retained in the body for long, it can lead to serious harm or even death.
- Hence, it is necessary to remove such harmful and waste substances from the body.
(6) Spinal cord
Answer:
- The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system and it is held within the vertebral column.
- It is slightly thick but gradually tapers towards the end.
- There is a thread like fibrous structure at its end. It is called the filum terminale.
- The long tubular cavity of the spinal cord is called the central canal. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- The spinal cord conducts impulses from the skin towards the brain and from the brain to the muscles and glands.
- It functions as a centre of co-ordination of reflex actions.
(7) Dialysis
Answer:
- The efficiency of kidneys can be adversely affected by injury, infection or decreased blood supply.
- If this happens, excess of toxic substances accumulates in the body and it can lead to death.
- If kidneys fail, nitrogenous wastes are separated from the blood with the help of a man-made machine.
- The process of separating the nitrogenous waste from the blood with the help of this machine is called dialysis.
- About 500 ml of blood is sent at one time through this machine. Purified blood is reinfused into the body of the patient.
FAQ: Life Processes in Living Organisms Class 9
1. What are “Life Processes in Living Organisms”?
Life processes are the essential activities carried out by living organisms to survive. These include nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, and reproduction.
2. What topics are covered in the Life Processes in Living Organisms Class 9 PDF?
The PDF includes:
- Characteristics of living organisms
- Nutrition in plants and animals
- Cellular respiration
- Transport system in plants and animals
- Excretion
- Homeostasis
- Control & coordination
- Reproduction in organisms
- Types of reproduction
- Growth and development
4. Is the Class 9 Life Processes PDF useful for exams?
Yes, this PDF is very useful for:
- Maharashtra Board Class 9 exams
- School internal tests
- Viva questions
- Revision before the exam
- MCQ, short notes, and long answer preparation
5. Is there a difference between “Life Processes” and “Life Processes in Living Organisms”?
Yes.
- Life Processes → General biological activities.
- Life Processes in Living Organisms → Included specially in Class 9 Science (Maharashtra Board) focusing on organisms’ functioning.
6. Can I download the Life Processes Class 9 PDF for free?
Yes, many educational websites including Sanskar Tutorials provide FREE downloadable PDFs of:
- Notes
- Exercises
- Extra questions
- Diagrams
- Important definitions
(You can add your PDF download link here.)
7. What are the important definitions in Life Processes Class 9?
Some key definitions include:
- Photosynthesis
- Autotrophic nutrition
- Cellular respiration
- Diffusion & Osmosis
- Transpiration
- Excretion
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
8. Are diagrams important in this chapter?
YES. Many exam questions come from diagrams like:
- Human digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Transport system in plants
- Mitochondria diagram
- Amoeba binary fission
- Photosynthesis process
9. How many marks come from Life Processes in the Class 9 exam?
Approximately 12–15 marks are asked from this chapter every year.
10. Is this chapter easy or difficult?
This chapter is considered easy to moderate because concepts are simple and many questions are memory-based.








[…] Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms […]