Table of Contents
Part 12 Study of Sound 9th Science Notes
Part 12 Study of Sound 9th Science Notes “Study of Sound” कक्षा 9 विज्ञान का एक महत्वपूर्ण अध्याय है, जो ध्वनि क्या है, यह कैसे पैदा होती है, कैसे चलती है, और हमारे कान इसे कैसे सुनते हैं—इन सभी अवधारणाओं को आसान भाषा में समझाता है। ध्वनि एक प्रकार की यांत्रिक तरंग (Mechanical Wave) है, जिसे चलने के लिए माध्यम (Medium) की आवश्यकता होती है। इस अध्याय में हम vibration, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, time period, loudness, pitch और Newton’s formula for speed of sound जैसे सभी महत्वपूर्ण टॉपिक्स को विस्तार में सीखते हैं।
स्टूडेंट्स को बोर्ड परीक्षा की तैयारी में मदद करने के लिए यहाँ “Study of Sound” का सरल नोट्स, परिभाषाएँ, फॉर्मूले, चित्रों का विवरण और सभी महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न उत्तर शामिल किए गए हैं। ये नोट्स स्कूल असाइनमेंट, रिवीजन और अंतिम मिनट की तैयारी के लिए बेहद उपयोगी हैं।
This article covers Class 9 Science Chapter: Study of Sound in a clear and simple language. Here you will get complete notes, definitions, formulas, diagrams explanation, important questions, and exam-oriented concepts that help you score full marks.
Chapter 11 : 9th Science Notes Maharashtra Board Part 11
1. Fill in the blanks and explain.
a. Sound does not travel through vacuum.
b. The velocity of sound in steel is greaterthan the velocity of sound in water.
c. The incidence of thunderstormin daily life shows that the velocity of sound is less than the velocity of light.
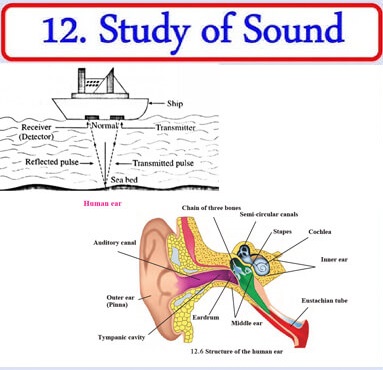
d. To discover a sunken ship or objects deep inside the sea, SONARtechnology is used.
2. Explain giving scientific reasons.
a. The roof of a movie theatre and a conference hall is curved.
- Sound waves get reflected from the walls and roof of a room multiple times. This causes a single sound to be heard not once but continuously. This is called reverberation.
- Due to reverberation, some auditoriums or some particular seats in an auditorium have inferior sound reception. This can be compensated with curtains.
- Ceilings of these halls are made curved so that sound after reflecting from the ceiling, reaches all parts of the hall and the quality of sound improves.
b. The intensity of reverberation is higher in a closed and empty house.
Answer:
- Reverberation occurs due to multiple reflections of sound.
- The furniture in the house acts as a sound-absorbing material.
- So if the house is closed and empty, a reflection of sound will be maximum and hence, intensity of reverberation is higher.
c. We cannot hear the echo produced in a classroom.
Answer:
- For distinct echoes, the minimum distance of the reflecting surface from the source of sound must be 17.2 m.
- Benches in the classroom are sound absorbing materials which prevent echo of sound.
- Because of these two reasons echo is not heard in a classroom.
3. Answer the following questions in your own words.
a. What is an echo? What factors are important to get a distinct echo?
Answer:
- An echo is the repetition of the original sound because of reflection by some surface.
- At 22°C, the velocity of sound in air is 344 m/s.
- Our brain retains a sound for 0.1 seconds Thus, for us to be able to hear a distinct echo, the sound should take more than 0.1 seconds after starting from the source to get reflected and. come back to us.
- We know that,
Distance = speed x time
= 344 m/s x 0.1 s
= 34.4 m - Thus, to be able to hear a distinct echo, the reflecting surface should be at a minimum distance of half of the above, i.e. 17.2 m.
- As the velocity of sound depends on the temperature of air, this distance depends on the temperature.
b. Study the construction of the Golghumat at Vijapur and discuss the reasons for the multiple echoes produced there.
Answer:
- Goighumat with a height of 51 metres and diameter of 37 metres with 3 metres thick walls is spread over approximately 1700 square metres.
- This meets the conditions for echo i.e. : 17.2 metres minimum.
- The dome of the golghumat is curved and hence, sound reflects multiple times before reaching the observer.
- This is the reason for multiple echoes being produced.
c. What should be the dimensions and the shape of classrooms so that no echo can be produced there?
Answer:
- Dimensions: The distance between opposite walls in a classroom must be less than 17.2 m so that the reflected sound returns to the observer within 0.1 s.
- Shape: The classrooms should have curved ceilings and walls so that the reflected sound is directed towards the observer instantly within 0.1 s
4. Where and why are sound-absorbing materials used?
Answer:
The sound absorbing materials are used in :
- School, cinema hall, concert hall, houses or places where quality of sound is important.
- In the absence of sound absorbing material the sound will undergo multiple reflection causing reverberation of sound.
5. Solve the following examples.
a. The speed of sound in air at O °C is 332 m/s. If it increases at the rate of 0.6 m/s per degree, what will be the temperature when the velocity has increased to 344 m/s?
Answer:
Given:
Initial speed of sound at 0°C 332 m/s.
Final speed of sound -344 m/s.
Rate of increase per degree rise in temp. = 0.6m/s
To find:
Temperature when speed is 344m/s
Formulae:
Increase in temperature
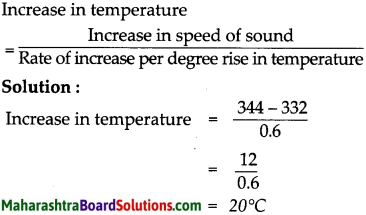
Temperature when the speed of sound is 344 m/sis 20°C
b. Nita heard the sound of lightning after 4 seconds of seeing it. What was the distance of the lightning from her? (The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s?)
Answer:
Given : Speed of sound (v) = 340 m/s
Time taken (f) = 4 sec
To find : Distance (s) = ?

The lightning has struck at a distance of 1360 m from the observer.
c. Sunil is standing between two walls. The wall closest to him is at a distance of 360 m. If he shouts, he hears the first echo after 4 s and another after another 2 seconds.
1. What is the velocity of sound in air?
2. What is the distance between the two walls? (Ans: 330 m/s; 1650 m)
Answer:
Given:
Distance of the closer wall (S1) = 660 m
Time of echo from closer wall = 4 sec
∴ Time taken (t1) = 4/2 sec = 2 sec
Time of echo from distant wall = 6 sec
∴ Time taken (t2) = 6/2 sec = 3 sec
To find :
Velocity of sound in air (y) =?
Distance between two walls (S1 + S2) = ?
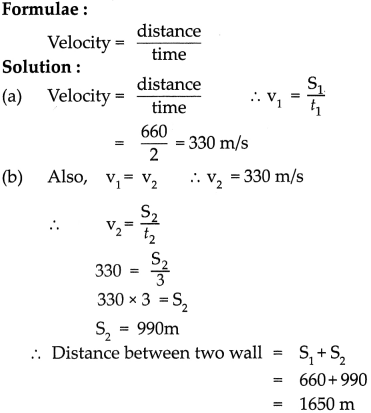
The velocity of sound in air is 330 mIs and the distance between two walls is 1650 m.
d. Hydrogen gas is filled in two identical bottles, A and B, at the same temperature. The mass of hydrogen in the two bottles is 12 gm and 48 gm respectively. In which bottle will sound travel faster? How may times as fast as the other? (Ans: In A; Twice)
Answer:
In A; Thrice
e. Helium gas is filled in two identical bottles A and B. The mass of the gas in the two bottles is 10 gm and 40 gm respectively. If the speed of sound is the same in both bottles, what conclusions will you draw? (Ans: Temperature of B is 4 times the temperature of A.)
Given:
Mass of Helium in bottle A = (mA) = 10gm
Mass of Helium in bottle B = (mB) = 40gm

The temperature of B is 4 times the temperature of A
Extra Question: Study of Sound Class 9 notes pdf maharashtra board
- How is ultrasound used in medical science?
Answer:
- Sonography: Sonography technology uses ultrasonic sound waves to generate images of internal organs of the human body.
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography is a test that uses ultrasonic sound waves to produce live images of your heart.
2. How will you reduce reverberation in public halls or buildings?
Answer:
(i) Reverberation in public halls or buildings will be reduced by using sound absorbing materials like curtains on wall, carpets on the floor.
(ii) By keeping the windows open, as sound will not get reflected.
3. The normal hearing range for humans is ……………………………… .20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
4. Bats can navigate in dark.
Answer:
- The ultrasonic sound produced by bats, gets reflected on hitting an obstacle.
- This reflected sound is received by their ears and they can locate the obstacle and estimate its distance even in the dark.
- Hence, bats can navigate in dark.
5. A SONAR system is installed in a ship.
Answer:
- A SONAR system determines the depth of the sea.
- It locates underwater hills, valleys, icebergs, submarines and sunken ships. It also locates the positions of other ships or submarines.
- Hence a SONAR system is installed in a ship.
6. Differentiate between Infrasound and Ultrasound
Answer:
| Infrasound | Ultrasound | ||
| (i) | Longitudinal waves whose are below 20 Hz are called Infrasound waves. frequencies Infrasonic or | (i) | Longitudinal waves whose frequencies lie- above 20,000 Hz are called Ultrasonic or ultrasound waves. |
| (ii) | Whales, elephants produce sound in the infrasound range. | (ii) | Bats produce (30 kHz to 50 kHz) frequency and dolphins produce ultrasound (100 kHz). |
7. Transverse waves and Longitudinal waves
Answer:
| Transverse waves | Longitudinal waves |
| (i) Particles of the medium vibrate at right angles to the direction of propagation of the wave. (ii) They produce crests and troughs. (iii) For transverse waves, a wavelength is made up of one crest and one trough. | (i) Particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave. (ii) They produce compression and rarefaction. (iii) For longitudinal waves, a wavelength is made up of one compression and one rarefaction. |
8. Suppose you and your friend are on the moon. Will you be able to hear any sound
Answer:
Sound waves need a material medium for their propagation. Since there is no atmosphere on the moon, we cannot hear any sound on the moon.
9. Explain with the help of a neat labelled diagram the working of human ear.
Answer:
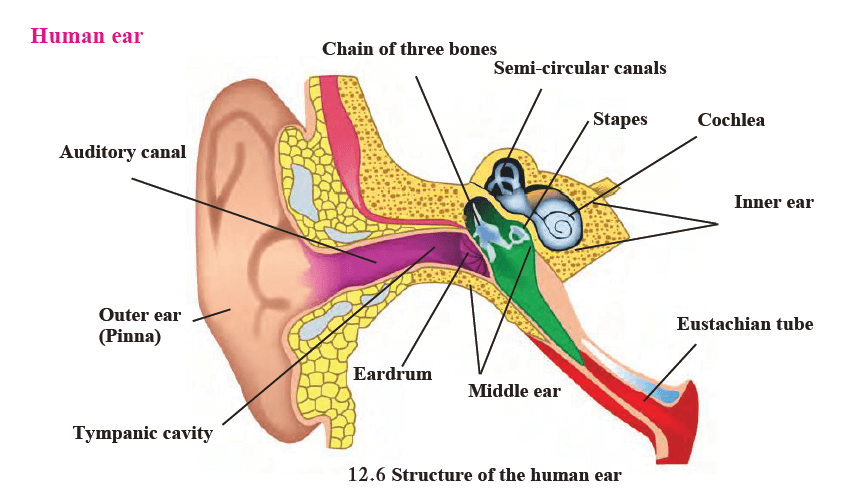
- The ear is an important organ of the human body.
- When sound waves fall on the eardrum, it vibrates and these vibrations are converted into electrical signals which travel to the brain through nerves.
- The ear can be divided into three parts:
(a) Outer ear
(b) Middle ear
(c) Inner ear.
(a) Outer ear or Pinna
The outer ear collects the sound waves and passes them through a tube to a cavity in the middle ear. Its peculiar funnel like shape helps to collect and pass sounds into the middle ear.
(b) Middle ear
There’ is a thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear called the eardrum. When a compression in a sound wave reaches the eardrum, the pressure outside it increases and it gets pushed inwards. The opposite happens when a rarefaction reaches there. The pressure outside decreases and the membrane gets pulled outwards. Thus, sound waves cause vibrations of the membrane.
(c) Inner ear
The auditory nerve connects the inner ear to the brain. The inner ear has a structure resembling the shell of a snail. It is called the cochlea. The cochlea receives the vibrations coming from the membrane and converts them into electrical signals which are sent to the brain through the nerve. The brain analyses these signals.
10. Write a short note on SONAR
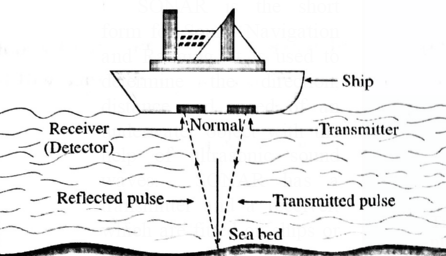
(i) SONAR is the short form for Sound Navigation and Ranging. It is used to determine the direction, distance and speed of an underwater object with the help of ultrasonic sound waves. SONAR has a transmitter and a receiver, which are fitted on ships or boats.
(ii) The transmitter produces and transmits ultrasonic sound waves. These waves travel through water, strike underwater objects and get reflected by them. The reflected waves are received by the receiver on the ship.
(iii) The receiver converts the ultrasonic sound into electrical signals and these signals are properly interpreted. The time difference between transmission and reception is noted. This time and the velocity of sound in water give the distance from the ship, of the object which reflects the waves.
(iv) SONAR is used to determine the depth of the sea. SONAR is also used to search underwater hills, valleys, submarines, icebergs, sunken ships etc.
11. Write a short note on Sonography. How is it misused?
Answer:
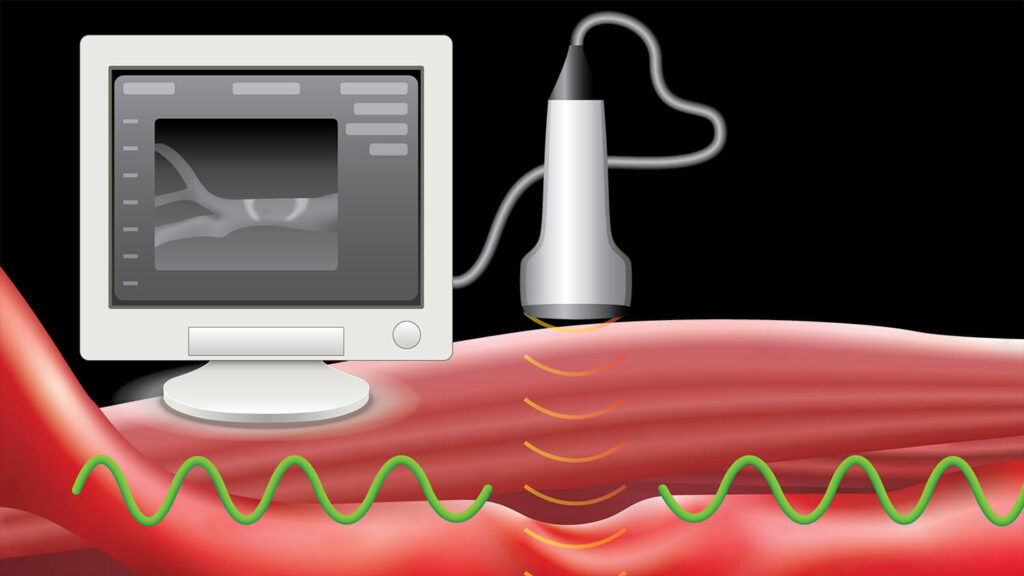
- Sonography technology uses ultrasonic sound waves to generate images of internal organs of the human body.
- This is useful in finding out the cause of swelling, infection, pain, condition of the heart, the state of the heart after a heart attack as well as the growth of foetus inside the womb of a pregnant woman.
- This technique makes use of a probe and a gel.
- The gel is used to make proper contact between the skin and the probe so that the full capacity of the ultrasound can be utilized.
- High-frequency ultrasound is transmitted inside the body with the help of the probe.
- The sound reflected from the internal organ is again collected by the probe and fed to a computer which generates the images of the internal organ.
- As this method is painless, it is increasingly used in medical practice for correct diagnosis.
- This technique is used by many people to find out gender of an unborn baby and this often leads to the incidence of female foeticide.
Full Explanation: Study of Sound exercise class 9
1. What is Sound?
Sound is a form of mechanical energy that travels in the form of vibrations through a medium like air, water or solids.
✔ Sound cannot travel in vacuum.
2. How Sound is Produced?
Sound is produced when any object vibrates (moves back and forth).
Examples:
- Guitar strings vibrate
- Vocal cords in humans vibrate
- Speaker diaphragm vibrates
3. Characteristics of Sound
a) Amplitude
- Maximum displacement of a vibrating body
- Determines loudness of sound
b) Frequency
- Number of vibrations per second
- Determines pitch (high/low sound)
c) Time Period
- Time taken to complete one vibration
- T = 1 / f
d) Wavelength
- Distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions
4. Speed of Sound
Depends on medium.
Fastest in solids → liquids → gases
Speed of sound in air (approx): 340 m/s
5. Audible Range
Humans can hear from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
6. Applications of Sound
- SONAR
- Ultrasound
- Communication
- Medical Imaging
📚 FAQs – Study of Sound Class 9 notes pdf maharashtra board
Q1. What is sound in simple words?
Sound is a form of energy produced by vibrations and heard by our ears.
Q2. What are the characteristics of sound?
Amplitude, frequency, wavelength, time period, loudness, and pitch.
Q3. What is the speed of sound in air?
The speed of sound in air is approximately 340 m/s.
Q4. Can sound travel in vacuum?
No, sound cannot travel in vacuum because it needs a medium.
Q5. What is the audible range of humans?
Humans can hear sounds between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Q6. What is the formula for frequency?
Frequency (f) = 1 / Time Period (T)









[…] Read : Chapter 12th: Part 12 Study of Sound 9th Science Notes […]
[…] Read : Part 12 Study of Sound 9th Science Notes […]